I am constantly looking for the article I need and losing it, then looking for it again. It should be added to the journal)) Self-diagnosis codes are read by the number of flashes of the “CHECK ENGINE” indicator when the “TE1”-“E1” terminals of the DLC1 connector under the hood or “TC”-“ are closed CG" of the DLC3 connector under the dashboard and the ignition is on. There is also a DLC2 connector in which "TE1" - "E1" are closed. If there is no fault, the indicator flashes at a frequency of 0.25 seconds. If there is a malfunction, the indicator displays first tens after 0.5 seconds, then a pause of 1.5 seconds and units with a pause of 0.5 seconds. If there are two or more codes, the pause between them is 2.5 seconds. After all codes are displayed, there is a pause of 4.5 seconds, and then the codes are repeated.
12 - Crankshaft position sensor (P0335) 13 - Crankshaft position sensor (P0335, P1335) 14 - Ignition system, coil No. 1 (P1300) and No. 4 (P1315) 15 - Ignition system, coil No. 2 (P1305) and No. 3 (P1310) 16 - Automatic transmission control system 18 - VVT-i system - phases (P1346) 19 - Accelerator pedal position sensor (P1120) 19 - Accelerator pedal position sensor (P1121) 21 - Oxygen sensor (P0135) 22 - Coolant temperature sensor fluid (P0115) 24 - Intake air temperature sensor (P0110) 25 - Oxygen sensor - lean mixture signal (P0171) 26 - Rich mixture (P0172) 27 - Oxygen sensor No. 2 31 - Absolute pressure sensor (P0105, P0106) 33 - ISCV valve (P0505) 34 - Turbocharging system 35 - Turbo pressure sensor 36 - CPS sensor (P1105) 39 - VVT-i system (P1656) 41 - Throttle position sensor (P0120, P0121) 42 - Vehicle speed sensor (P0500) 43 — Starter signal 47 — Auxiliary throttle position sensor 49 — Fuel pressure sensor (D-4) (P0190, P0191) 51 — Switch status 52 — Knock sensor (P0325) 53 — Knock signal 55 — Knock sensor No. 2 58 — SCV drive (D-4) (P1415, P1416, P1653) 59 - VVT-i signal (P1349) 71 - EGR system (P0401, P0403) 75 - Power steering pressure sensor (P0550) 78 - Injection pump (D-4) 89 - ETCS drive (P1125, P1126, P1127, P1128, P1129, P1633) 92 - Cold start injector (D-4) (P1210) 97 - Injectors (D-4) (P1215)
You can also reset the errors by pulling out the efi fuse for a few seconds (the block under the hood on the right).
engine control automatic transmission operating mode indicators headlights interior lighting air conditioning with automatic control radio radio warning system for lights not turned off remote control of central locking ABS (VSC)
Toyota cars equipped with electronic control units (ECUs) of the engine, automatic transmission, ABS, etc., have the ability to perform self-diagnosis. The operating principle of this system is as follows:
- If a deviation from the normal operating mode occurs, the sensor recording it is turned off.
- A bypass program is activated in the ECU, allowing the vehicle to continue operating. When this program is turned on, the alarm light on the display lights up or the system operation lamp in which a breakdown is detected blinks.
- When the malfunction is eliminated (spontaneously or as a result of repair), the bypass program is disabled and the system continues to operate as normal.
- Information about a malfunction that occurs is stored in the form of a special code, which can later be read.
On modern Toyota Corolla cars, the ECU is able to distinguish faults according to the degree of importance for operation, and information about “light” deviations is not recorded. For example, if dirt gets on one of the ABS sensors while driving, and after washing it off, the sensor returns to normal operation, this deviation will not be recorded.
The diagnostic system is very convenient when repairing a car, thanks to it you can quickly identify the cause of problems.
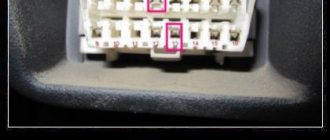
Connectors for diagnostics of Toyota Corolla cars
For self-diagnosis of Toyota Corolla cars, special diagnostic connectors (DLS - DataLinkConnector) are provided, the type and location of which depend on the model and year of manufacture of the vehicle.
DLS 1 is a rectangular plastic box located under the hood of the car on the left. This connector has a corresponding designation on the housing - “DIAGNOSTIC”. Self-diagnosis is carried out using the “CHECK” light located on the instrument panel, the corresponding control lights for vehicle systems or other signaling devices.
Salon
The salon is well equipped technically. The front seats are designed in such a way as to maximally protect the driver and passengers from all kinds of injuries. The rear row of seats cannot boast of its comfort, especially for the five-door version. The instrument panel is conveniently and ergonomically located; all instruments are in a good field of view for the driver. The steering wheel is power-assisted and adjustable depending on the driver’s needs; there are buttons on it that control the audio system,
Methods for reading information during car self-diagnosis
There are two main ways to read error codes: using improvised means or using special equipment for car diagnostics.
- In the first case, self-diagnosis is performed by shorting the corresponding terminals of the DLC connectors with a wire or using a regular straightened paper clip. To do this, find the connector marked DIAGNOSTIC and open its cover. On the back of the cover there is a pin marking diagram. Using a wire, we close the terminals “E1” and “TE1” on DLC 1, or the terminals “TC” and “CG” on DLC 3. After this, turn on the car’s ignition and observe the blinking of the corresponding lights on the instrument panel.
- For diagnostics, special diagnostic devices can also be used: scanners or testers. Some service stations have special diagnostic computers. These devices are expensive, but in addition to full diagnostics, they allow programming of various systems and reading signals coming from various nodes in real time.
Types of two-digit codes
For self-diagnosis of cars, two types of two-digit codes are most often used: the first is type 09; the second is type 10.
You can determine what type your car supports and whether there are any recorded errors in its operation as follows:
Frequent and continuous flashing of the warning light, when the flash and pause last for 0.5 seconds each, indicates that the vehicle is using type code 09. If when using this code the light flashes more than 11 times, then no fault records were detected.
When using codes of the second type, the light blinks at intervals of varying durations. The absence of faults during self-diagnosis is indicated by continuous flashing at intervals of 4.5 seconds. An example of reading codes of this type: flash - pause - flash - long pause - flash - this is code 21.
Two-digit system codes
Powertrain fault codes
Decoding engine fault codes for type 09:
11 — lack of power supply to the valve control unit; 12 and 13 - no engine speed signal is received; 14 - no feedback is received from the negative contact of the ignition coil or, if there are two of them, then from coil No. 1; 15 - no feedback from the negative contact of ignition coil No. 2; 16 - no signal is received from the automatic transmission ECU; 17 and 18 - unacceptable value of camshaft position No. 1 and No. 2; 21 — incorrect signal from the oxygen level sensor; 22 - unacceptable temperature value of the power unit; 23 and 24 - incorrect indicator of intake air temperature; 25 — lean air-fuel mixture; 26 - too rich air-fuel mixture; 27, 28 and 29 - incorrect signal from the additional oxygen sensor; 31 — unacceptable value of air flow or pressure of the intake manifold; 32 — incorrect response of the air flow sensor; 34 — boost malfunction; 35 — unacceptable value of intake manifold pressure (vacuum sensor); 38 - incorrect signal from the fluid sensor in the automatic transmission; 41 — incorrect response of the throttle position sensor; 42 - unacceptable value of the speed that the car develops; 43 - lack of starter signal on the engine ECU; 46 - malfunction of solenoid valve No. 4 or its circuit; 47 - breakdown of the additional sensor that fixes the position of the throttle or its circuit; 48 — malfunction of the additional fuel supply system; 51 - there is no idle signal from the sensor displaying the throttle position; 52 and 55 - incorrect feedback from the knock sensor; 53 - failure of the knock sensor control circuits; 61 - malfunction of the speed sensor and its circuit; 62-65 - malfunction of solenoid valves No. 1-4 or the corresponding circuit; 67 - malfunction of the O/D switching sensors or its circuit; 71 — breakdown of the exhaust gas recirculation system; 72 - malfunction of the fuel cut-off solenoid; 77 - malfunction of the pressure control solenoid or its circuit (in automatic transmission); 78 - there is no signal from the fuel pump or a malfunction of its circuits; 81—85 — malfunction of circuits in various parts of the robot box; 86 - breakdown of sensors that record engine speed; 88 - malfunction of the electrical circuit between the power plant control units and the automatic transmission; 89 — malfunction of the electrical circuit between the power plant control units and the robot box; 99 - no faults. Decoding engine fault codes for type 10: 1 - normal operation; 2 — unacceptable air flow value; 3 — incorrect switch signal; 4 - unacceptable antifreeze temperature value; 5 — incorrect oxygen sensor signal; 6 — unacceptable engine speed; 7 — incorrect response of the throttle position sensor; 8 — invalid air temperature sensor signal; 9 — incorrect signal from the sensor recording the vehicle speed; 10 — there is no signal to turn on the starter; 11 - breakdown of the air conditioner or position N in the automatic transmission.
OBD standard codes
Some Toyota Corolla cars support the OBD standard, which provides for error indication using 5-digit codes: one alphabetic character and four numeric ones.
The first character of this code is called the Alpha pointer and indicates the system in which the fault occurred:
- P - engine or transmission;
- B - car body;
- C - suspension;
- U is a network system.
The following numbers indicate the exact location and classification of the problem.
To diagnose problems in cars that support this protocol, it is recommended to use special scanners, testers, or connect to a PC using special programs.
Specifications
Models for the domestic market released in 2005 were equipped with gasoline engines with the following displacement:
- 1.4 liters with a power of 97 hp;
- 1.6 liters with a power of 110 hp;
- 1.8 liters with a power of 192 horsepower (installed on the sport version).
As for the transmission, the ninth generation was equipped with a five-speed manual transmission and a four-speed automatic.
In our market you can find Corollas that were produced for other countries, with diesel engines of 1.4 and 2.0 liters.
The front part has MacPherson struts, which are well known among Corolla lovers, and the rear part has a semi-independent torsion bar suspension with shock absorbers that were innovative for that time. Thanks to this suspension design, the car has excellent directional stability and perfectly smooths out all the irregularities that arise on the road.
The braking system of the car is designed as follows: ventilated disc brakes are installed on the front wheels, and non-ventilated disc brakes are installed on the rear wheels. All trim levels are equipped with an ABS system.
How to reset error data after diagnostics?
After carrying out diagnostics and reading the necessary information about vehicle breakdowns, it is recommended to erase the error data for correct operation of the system. To do this, some models provide a method for removing fuses (for different models this may be “HAZ-HORN”, “STOP” or “EFI”). The 30-second method of disconnecting the negative terminal of the battery is suitable for all cars. This method is not recommended for cars that have systems for adjusting to driving style.
Each car is characterized by some kind of damage and malfunction of the engine and other mechanisms. Naturally, Toyota Corolla is no exception. Most often, at the first problem, the car is taken to a service station for diagnosis. However, the Corolla is one of the most thoughtful and sophisticated cars of our time. Its developers have provided the ability to identify problems with their own hands.
Diagnostic connectors
Electrical equipment that directly interacts with the engine works constantly, since not only the performance of the car, but also its overall operation depends on it. Naturally, each mechanism is characterized by certain malfunctions that appear under certain circumstances.
An interesting fact is that they cannot always be recognized, therefore, to identify problems, owners of Toyota Corolla (starting with 100 bodies, including the EE103 station wagon, and ending with 150) have the opportunity to conduct self-diagnosis. It is carried out using diagnostic connectors, which are usually referred to as DLC (Data Link Connector).
These adapters are located in three places on the machine. DLC1 is located in the engine compartment in the upper right corner, DLC2 is located in the passenger compartment under the dashboard and steering wheel. The difference between the first and the second lies in the configuration, since diagnostics will require special equipment. In addition, through DLC1 you can check the condition of parts while the engine is running, while DLC2 is best used with the engine running. In addition, there is a DLC3 connector, which is located under the front door on the driver's side. It can be found on cars with a robotic gearbox.
It is important to note that Toyota Corolla diagnostic connectors may be located in slightly different places depending on the body type and, accordingly, the year of manufacture. For example, on the 110 model, produced until 2001–2002, DLC1 is located closer to the engine, and its location under the hood can be found significantly lower than in the 120 version, which appeared on the Russian market in 2003.
Differences in the given configurations
These models have the following features:
- R0 - basic, equipped exclusively with safety equipment: anti-lock braking system (ABS) and 2 airbags;
- R1 is a more popular option, also equipped with air conditioning and power accessories;
- R2 is the top version, equipped with climate control, an optical instrument panel, and a velor interior.
American version
There are quite a lot of Toyota cars imported from America on the Russian automobile market. These sedans were assembled in Japan and equipped with a 1.8-liter 135-horsepower engine (ZZ series) with a manual or automatic transmission. This option differs from the European version not only in the engine, but also in appearance, rear drum brakes, and softer suspension.
Russian car enthusiasts are not recommended to purchase the Corolla 120 model, designed for the American market:
- This version of the Toyota car (its parts) has many differences with the European version; when something breaks, then any part (both just stabilizer bushings and body elements) will need to be ordered;
- Their engines do not respond well to our gasoline, and they usually use low quality oil (common problems with cars intended for the American market).
Reading information
Obtaining data on the presence of faults is carried out by reading information. This procedure is carried out using one of two methods. The first involves closing the necessary terminals of the diagnostic connector using a wire or an ordinary paper clip. To set up the device, you need to open the cover on the DLC with the inscription Diagnostic, close a pair of pins (for DLC1 these are E1 and T1, and for DLC3 – TC and CG). After this simple procedure, you need to turn off the ignition and then just look at what signals the instrument lights are giving.
Fault codes and their types
Self-diagnosis of Toyota Corolla 150 involves working with two-digit codes. There are only two types: 09 and 10. You can find out which option is being used by looking at the signals.
In the first case, a constant, rapid ignition of the light bulb should appear, with the length of the flash and pause being about half a second. In this case, the absence of malfunctions is indicated by blinking more than 11 times. The second type is present in the machine if the signal appears at different intervals. You can find out that there are no problems by constantly blinking at a stable interval of approximately 4.5 seconds.
There can be about 200 faults. Signal types 09 and 10 mostly specialize in one or another group of problems. For example, the first of these systems works with components of the 1ZR engine, which appeared on cars with a 130 body, and was later retained on 150 and later models. The most common problems are problems with a faulty or damaged air sensor. In addition, this also includes many shortcomings in the operation of the central panel (pointers, their incorrect display, and so on).
As for code 10, it can’t say much about the power plant as a whole (about 10 times less than 09).
Of course, the signals still concern the same air flow and temperature, but greater emphasis is still placed on the anti-lock and traction control systems. At the same time, problems with both ABS and TRS are divided into smaller ones.
Features of operation
Gasoline power units require major repairs after 250,000 kilometers, and in order for the engine to operate without problems for as long as possible, the oil must be changed every ten thousand kilometers, and the spark plugs must be changed every 30,000 kilometers. It is also recommended to change the oil in the gearbox in a timely manner. The problem that owners of a Toyota Corolla released in 2005 most often encounter is the rapid wear of the bushings on the steering rack and the timing belt tensioner also often fails.
OBD standard
A number of Toyota Corolla cars (including the 150 body) work with the OBD II standard. Without pinouts, it is quite difficult to understand exactly what errors occurred, so you need to know the exact designations of the 5-digit code: P – power unit/gearbox, B – body, C – suspension, U – network. The numbers that come after this code indicate the specific location of the malfunction. Diagnostics using the OBD 2 system are best carried out using special programs used on computers, as well as testers or scanners.
Appearance
The body of the 2005 Toyota Corolla has smoothed shapes and slightly elongated headlights, making the car's appearance more rapid. The manufacturer initially did not focus on the body, but paid more attention to the technical part of the car, so the body did not have a stylish and memorable appearance. Overall dimensions differ depending on the body type, for example, a hatchback has the following dimensions:
- Length 4180 mm;
- Width 1710 mm;
- Height 1475 mm;
- Ground clearance 15 centimeters.