How to diagnose the error?
Now almost every car has many electronic sensors that transmit information about an existing malfunction to the engine control unit. Based on this, a specific error code is generated, which is needed for diagnosing and eliminating the malfunction.
There are several indicators that indicate different problems:
Computer diagnostics
Scanners are necessary to diagnose the ECU and all components of the car.
The best results are achieved when tested on professional dealer devices .
In most cases, a simple scanner to read faults from engine management systems.
General Rav 4 error codes are determined using the OBDII protocol.
To consider malfunctions in the operation of the car, the technician must perform the following actions :
And only after this the wizard analyzes and eliminates errors identified during the diagnostic process.
How to carry out self-diagnosis of a car?
Toyota cars usually have 3 blocks of dynamic connectors: DLC 1, DLC 2 and DLC 3. These blocks can be either under the hood or inside the cabin. It all depends on the year of manufacture of the car. Without a special scanner, you can carry out self-diagnosis of the car. This will require wire. It should be bent like the letter P.
To carry out diagnostics, first of all, you need to turn off the ignition in the car. Next you need to do the following:
Next you need to start the car and check the CHECK indicator. Based on this, the error number can be determined.
It is not difficult to determine the error code. You need to count how many times the indicator flashes at intervals of half a second or less. If the light stops blinking for about 1.5-2.5 seconds, then the next blinking will indicate the second digit. For example, the indicator may blink 2 times with an interval of half a second, then pause for 1.5-2.5 seconds and blink 3 times again. This means error code 23.
There may be a situation when several problems are detected at once. Then there will be more than one code. A pause between flashes of 2.5-4.5 seconds means a transition to the next code.
If the indicator blinks more than 11 times without pauses, then there are no problems with the transmission or engine.
It will be easier for the driver to determine the essence of the problem if there is a special auto scanner for diagnostics. It can be used to configure and diagnose the on-board computer. Without a scanner, you need to decipher error codes yourself using a table.
There are errors mainly related to malfunctions:
On Toyota Rav 4, the error code usually consists of five characters, but there are also two-digit ones.
Car scanners
It's easy to get lost among the variety of scanning devices.
To diagnose Rav 4 error codes, both hardware types of devices and scanners from the adapter are used.
Scan Tool Pro is one of them. This instrument is easy to operate and suitable for initial analysis. The scanner is universal . Connects to any type of device running on operating systems such as iOS, Android, Windows, via the standard OBDII protocol .
Pros of Scan Tool Pro:
The device detects most faults. And yet, the scanner has one serious drawback - there are too many fake devices on the market. It will be difficult for an amateur to distinguish the original from the fake.
Launch CReader V+ is already equipped with a bright LCD screen and does not require additional connection to devices. The test results are displayed on the screen in the form of text and graphic blocks reflecting the dependence of the values.
Advantages of Launch CReader V+:
The device has one drawback - the screen is too small .
Delphi DS150E is the leader among affordable automotive scanners. The device is universal and works using the Generic OBD or eOBD protocols , and also scans the available car units. When performing dynamic scanning, data is transferred to a memory card, which is installed in a special slot.
The Delphi DS150E has many features for an affordable automotive scanner, often used in service stations. Some users consider the too large size of the device to be a disadvantage.
Common mistakes on Toyota Rav 4
| Error code | Decoding |
| c1298 | Detection of this fault code means that the pressure control solenoid device is not functioning properly. It is necessary to check whether the mechanism is intact. If yes, then you need to check the wiring and then the all-wheel drive control module |
| S1201 | This error code is recorded when the engine speed is below the set limit. It is necessary to check the idle speed sensor and diagnose the shafts. It is necessary to check the power unit. |
| P1047 | Code P1047 may appear when a problem is detected in the Valvematic module settings. It is possible that power supply circuit B1 is damaged. |
| P2646 | The detected fault code makes it clear that the VTEC sensor does not receive information about the presence of pressure, and the valve opens |
| P1750 | Code P1750 appears when there is a problem with the brake system control unit. |
| P0138 | Combination P0138 is a sign that the oxygen output level in the first tank has been exceeded. |
| P2757 | When P2757 is detected, you should check the operation of the DSU sensor on the transmission. |
| P1604 | Code P1604 may appear on cars produced in 1992, 1997, 1993, when there was an unsuccessful attempt to start the engine. This can happen for several reasons: |
Toyota car diagnostics
Diagnostics are available on cars of the entire Toyota model range and are divided into two types:
Before starting electronic diagnostics, the driver must ensure that all systems and main mechanisms of the Toyota vehicle are in working order. To do this, you should check the fuses, electrical wiring, and also examine the connections and components of the vehicle for damage.
If any serious problem is detected, it must be eliminated, and only then carry out computer diagnostics, which can happen:
Step-by-step self-diagnosis
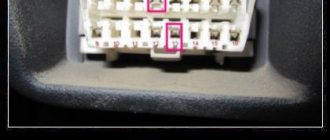
For self-diagnosis, the driver needs to work with the DLC 1 and DLC 2 connectors. This abbreviation stands for Data Link Connector, which in English means a connector for connecting data. DLC 1 looks like a plastic box with a lid on top. It is located under the hood, most often on the left. It is easy to find by the inscription Diagnostic.
Diagnostic signature on the connector
In older models, the diagnostic connector is shaped like a yellow circle and is located near the battery. There are no DLC2 parts in cars like the Corolla AE 100.
Fault codes for older car models: Toyota Corona 1992, Karina 1992-97, Toyota Mark are read only by flashing indicators.
In new models, DLC 2 is located directly in the cabin, under the dashboard and “at the feet” near the steering wheel. Most often it is round and is used during inspections carried out using special equipment.
Round DLC2 connector
When performing self-diagnosis by shorting individual contacts of the connector, only by connecting them in the required sequence can you obtain the correct code for decoding.
The following steps will help you find out if there are faults in the engine and/or gearbox system:
DLC 1 connector diagram
Everything is fine with the car and no damage to the internal combustion engine or transmission was detected if:
Any other combinations of light bulbs indicate a malfunction in the engine systems, gearbox or other mechanisms in the car.
If the circuit on the back of the cover has been erased, you cannot find the contact or you are not sure that you have closed the right one, you must:
It will be more convenient if someone helps you monitor the light bulb while you change the position of the wire.
Recognize fault codes using two flashing light systems.
The first setting option will allow you to find out errors indicated by a two-digit code (type 09):
Using the 10th setting type, unambiguous codes are determined. Here the light “blinks” the exact error number.
This code should be “read” according to the following rules:
The video shows diagnostics using type 9 code, author Dmitry Kuzmin:
Failures in the ABS system are determined using the same scheme, but the TC and E1 terminals are closed. The SRS and 4WS fault codes are read by the corresponding sensor with the same contacts closed as in the ABS.
Photo gallery “Self-diagnosis of Toyota cars”
Diagnostic connector DLC 1
Contacts TE1 and E1 on the connector
Closing contacts
Location of the connector under the hood
How can I reset the error?
After diagnostics, you need to erase the fault code. This can be done by following the following step-by-step algorithm:
You can also reset error codes using technical means. For example, a laptop can help with this. This will require a special program designed for these purposes.
This article describes the most common error codes. If there is an error that is not in the material, we recommend contacting the service.
Self-diagnosis - step-by-step instructions
Professional car diagnostics at a specialized service center is not cheap. In addition, many car owners simply do not have the opportunity to use such services, since they live far outside large cities, and they have no desire to turn to “garage” specialists.
In such cases, self-diagnosis methods come to the rescue. Only basic skills are needed, so even beginners can figure it out. For example, to check engine operation, the procedure is performed in the following order:
If your car uses a DLC3 connector, you need to close contacts TC and CG.
Technical description and interpretation of error P0105
OBD II diagnostic code P0105 is identified as a malfunction of the manifold absolute pressure/barometric pressure sensor circuit. Set when the PCM detects voltage from the MAP sensor that does not correspond to the current engine load or throttle position. It may also mean that the signal from the MAP sensor does not correlate with the throttle position sensor (TPS) signal voltage.
As engine load changes, intake manifold pressure also changes in response to changing demand. As a result, the MAP sensor generates voltage signals based on pressure changes. Which the PCM uses to calculate fuel delivery and adapt to ignition timing to keep the engine running at peak efficiency.
To monitor the accuracy of the MAP sensor readings, the PCM uses other sensors, most notably the throttle position sensor (TPS). Thus, if the PCM detects a "mismatch" between the signals from the MAP and TPS sensors. This will be recognized as a fault condition and code P0105 will be set.
In a properly operating system, the PCM expects to detect a change in signal voltage from the MAP sensor immediately after a change in throttle position. But this only happens if the MAP, TPS sensors and their associated circuits are working correctly.
A faulty TPS sensor can also cause the P0105 code to set when its signal voltage does not match the MAP/BARO sensor signal voltage.
Symptoms of malfunction
The main driver symptom of P0105 is the MIL (Malfunction Indicator Light). It is also called Check engine or simply “check light”.
They can also appear as:
The error is serious because when it appears, problems with the engine may occur. But if there are no symptoms and only the Check Engine light is on, the OBD-II system can be restarted and the vehicle will continue to operate normally.
Conclusion
Computer diagnostics of a Toyota Corolla E150, 120 or other modification for most modern cars is performed through the OBD II connector, and during the test the device can show a code with the index P, which indicates the presence of problems. When such errors appear, it makes sense to check the engine of a Toyota Corolla released in 2008 or later, and conduct a detailed check of the condition of the gearbox, clutch, electrical system or other system, depending on the specific code. The error is reset after the problem is detected and corrected; cleaning is done by issuing a command from the scanner or resetting the terminal: in the first case, the result will appear instantly.
Diagnosis and problem solving
Inspect any visible damage to sensors, wiring, and connectors. Then start the diagnostic procedure using the scanner. To determine if P0105 is the only fault code, if not, it may be worth looking into other trouble codes first.
If no problems are found with damaged or corroded connectors, perform a thorough inspection of all associated wiring. Repair or replace damaged wiring as necessary.
Check for clogged air filter and damaged catalytic converter. You should also look for damaged or disconnected air intakes, displaced or broken vacuum lines, and obstructions in the intake tract. Replace hoses, air lines, filter element or vacuum lines as necessary.
Checking the MAP sensor
If the code remains, check the reference voltage at the MAP sensor connector. Also check for ground and continuity, especially in the signal wire between the PCM and the MAP sensor connector. If resistance is infinite, repair open in the MAP signal circuit.
If continuity is normal, check the MAP sensor by applying vacuum to it. The voltage from the MAP sensor should gradually decrease from 5 volts to 1 volt or slightly less. And increase back to about 5 volts as the vacuum is released. If the signal voltage does not change within manufacturer specifications, replace the MAP sensor.
Often, MAP sensor readings can get stuck at 4.5 volts, no matter how much vacuum is applied. This means there is a short between the signal wire and the 5-volt reference wire. If necessary, repair the wiring to eliminate the short circuit.
If there is no voltage in the signal wire when you disconnect the MAP sensor connector, there is an internal short circuit and the sensor must be replaced.
In some cases, the PCM may be faulty or in the process of failing. But this happens extremely rarely. Therefore, before replacing it, it is better to check everything carefully again.
Toyota automatic transmission fault codes
To read the codes, you need to count the number of times the O/D OFF light comes on with the ignition on and terminals TE1-E1 in the DLC1 connector (in the engine compartment) or TC-CG in the DLC3 connector (in the passenger compartment) closed. Check that upshifting is not prohibited (the O/D OFF indicator should not be illuminated).
Codes and decryption:
- 11 – all indicators are normal;
- 37 / P1705 – malfunction of the transmission input shaft speed sensor;
- 38 – incorrect signal from the transmission fluid temperature sensor;
- 42 / P0500 – speed sensor or output shaft speed sensor;
- 44 – failure of the rear output shaft speed sensor or speed sensor;
- 46 / P1765 – failure of the hydraulic accumulator pressure control solenoid;
- 61 – malfunction of the front output shaft speed sensor or speed sensor;
- 62 / P0753 – problems with the first solenoid;
- 63 / P0758 – problems with the second solenoid;
- 64 / P0773 – malfunction of the torque converter locking clutch solenoid;
- 67 – incorrect readings of the transmission input shaft speed sensor;
- 68 – breakdown of the torque converter locking clutch solenoid;
- 73 – malfunction of the center differential locking clutch solenoid.
The CHECK, 4WD, VSC indicators came on in Toyota RAV4 (solved) - 1 answer
Some time later: Yesterday I was driving and suddenly, in a turn, symptoms of a blocked central diff appeared; we don’t have it; it turns out that the rear-wheel drive coupling was rigidly blocked! From which one? The fucking homosexuals from the previous service couldn’t unscrew the filler plug and “dripped” as much as they could and didn’t say anything. I drove it on a dry highway, apparently I overheated the clutch several times, and that’s why it jammed.
What could lead to this? And today I was driving in a straight line and the check light came on: Who can tell me what? I read the blue forum, thought about it, and came to the conclusion that the clutch died, the ECU somehow sensed its inadequate operation and completely cut off the rear-wheel drive connection.
Rav 4 Lights up Check the 4wd System and Check Engine Lights on Rav 4 Check Lights on Check 4wd Check Engine on Rav 4 Check Engine Lights on Check the 4wd System
Error: "Check AWD system, TRC system is not working" on Toyota Rav4.
you need to press the button on the panel on the left side.
But when I pressed this button, a new message “Check AWD system” appeared .
The first thing that came to mind was to remove the terminal to clear the error. This action did not help.
Here I got a little worried, because after reading on various forums the assumptions were not reassuring.
Some wrote that it was necessary to look at the spark plugs
, the engine , the fuel pump ,
others that it was something with
a variator
, and many more assumptions. They suggested going to an official dealer, but we are not looking for easy ways.
I read in one of the posts that such glitches can occur along the power supply line. You could check this on your own, which is what I did.
As a result, the reason was found, it was simply a 7.5 A
Under the number 14
responsible for the reversing lights.
After installing the working fuse, you must reset the terminal again to clear the errors.
After this, the errors no longer appeared. I will be glad if this information helps you.
ELECTRONIC STABILITY SYSTEM (ESP) (if equipped)
• When accelerating hard or driving on slippery road surfaces, the vehicle's wheels may begin to slip and slide laterally. The ESP electronic dynamic stabilization system is capable of detecting a loss of vehicle directional stability using sensor signals and helping the driver keep the car on the desired trajectory. The dynamic stabilization system controls the wheel brakes and, if necessary, reduces the power developed by the vehicle's engine.
– When the ESP system is turned on, the indicator lamp for deteriorating road traction, located on the dashboard, begins to flash.
– When only the traction control system TCS, which is part of the ESP system, is activated, the indicator lamp for poor traction of the road surface also begins to flash.
– If the indicator lamp for poor grip of the road surface flashes, this means that the vehicle is moving on a slippery road.
ESP system failure warning
If the normal functioning of the ESP system is disrupted, the indicator lamp for deterioration of road adhesion properties and the indicator for turning off the dynamic stabilization system (ESP OFF), located on the dashboard, light up. As long as these lamps are on, the vehicle's dynamic stabilization system will not function.
• Vehicle Dynamic Stability Program (ESP) uses an Active Brake Limited Slip (ABLS) system to improve the vehicle's traction properties. ABLS operates similarly to a limited-slip differential and is activated when one of the drive wheels encounters a low-traction surface and begins to slip. The ABLS system, by braking the slipping wheel, provides a corresponding increase in torque on the other wheel of the axle, which has better traction with the supporting surface.
• When the ESP system is turned off, none of the functions of this system will operate, and the TCS traction control system will not work. However, the Active Wheel Braking System (ABLS) and the Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) will continue to function even when the ESP system is turned off. When the ABLS system is activated, the warning lamp will flash and you may hear a characteristic noise and/or feel a pulsating force on the wheel. brake pedal. This is normal and does not indicate a system malfunction.
• Vehicle Dynamic Stability also uses FBS (Fade Brake Support) (if equipped), which provides shorter braking distances when the brakes are hot. In addition, the FBS system increases driving safety on long descents when the driver applies frequent braking as necessary.
• During the operation of the dynamic stabilization system (ESP), you may feel a pulsation of force on the brake pedal and hear a characteristic noise or feel vibration from under the hood of the car. This is normal and confirms that the ESP system is functioning properly.
• The diagnostic program built into the ESP control unit checks the serviceability of the system every time the engine is started and the vehicle is driven at low speed in forward or reverse gear. During self-diagnosis of malfunctions, you may hear a characteristic noise and/or feel a pulsation of force on the brake pedal. This is normal and does not indicate a system malfunction.
• In some cases it may be useful to turn off the ESP system to allow the wheels to spin:
– When driving in deep snow or wet ground;
– When the car rocks back and forth when stuck in the snow;
– When driving with snow chains installed.
1. ESP SWITCH (if equipped)
Check Engine light is on (engine error): causes and best solutions to the problem
On the road, situations often arise when the check light is on and the message “ engine power limited ” is displayed. With this signal, the on-board computer responds to a number of breakdowns, which include: At car services, injectors are cleaned on special ultrasonic cleaning stands or completely replaced. You can continue driving with one or two clogged injectors at low speeds.
It will be easier for the driver to determine the essence of the problem if there is a special auto scanner for diagnostics. It can be used to configure and diagnose the on-board computer. Without a scanner, you need to decipher error codes yourself using a table.
The occurrence of extraneous sounds when the engine is running
Many car owners complain about the water pump. In its standard version it has design flaws. Because of this, the pump may begin to hum when the car’s mileage barely reaches 15-20 thousand km. In most cases, the pump is replaced under warranty.
Water pump
More serious extraneous sounds occur when fingers tap. This problem can occur with a mileage of 60 thousand km, but usually does not appear until 150-180 thousand km. The problem of knocking fingers needs to be solved by disassembling the engine and replacing them along with the pistons.
Engine does not develop full power Toyota RAV4
Tool:
Parts and consumables:
Notes:
If the engine does not develop full power, check the components and mechanisms in the sequence described below to troubleshoot the problem.
1. The oxygen sensor (lambda probe) may not be functioning properly. Replace it with a new one. Contact the service center for a more thorough check by specialists of the exhaust gas system components to find faults and eliminate them.
2. Remove the ignition distributor and check the shaft play in it, the serviceability of the runner, and the distributor cap. If the play is large or there is significant damage or wear to the housing and parts, replace the distributor.
3. Faulty high-voltage spark plug wires can also cause unstable operation of the ignition system. Therefore, check the wires for cuts, breaks, etc. Replace faulty high-voltage wires.
4. Check the spark plugs for wear or incorrect gaps. How to remove candles is written in the first part of the article here. Then check the gap of each spark plug using a spark plug gap gauge. Replace faulty spark plugs with new ones.
5. The cause may also be a malfunction in the fuel injection system or engine management system. To find the exact problem and fix it, contact a specialist service center.
6. Check if the engine air filter is clogged. Replace it if it is filled with dust.
7. Then look to see if the brakes are stuck. Bleed the brake system.
8. The fluid level in the automatic transmission may not be correct. Add transmission oil to the automatic transmission.
9. Check clutch slippage (“slips”). The release bearing or other clutch part may be faulty.
10. Check the fuel filter for clogs or foreign particles in the fuel system. Replace the clogged filter element.
11. Contact a specialist service center to check the exhaust gas neutralization system to look for a possible malfunction.
12. Then check the compression in the cylinders and compare it with the values given in the technical documentation, because uneven or low compression in the cylinder can also cause unstable engine operation. How to check compression in engine cylinders is written here.
The article is missing:
Source:
P0137, P0157
P0137, P0157 – low voltage in the oxygen sensor circuit (bank 1, bank 2 sensor 2). Causes of errors P0137, P0157:
New and Old Lambda Sensor If, during active air-fuel ratio control, the target ratio is rich but the heated oxygen sensor output voltage is less than 0.21 V (lean), the ECM treats this as an excessively low sensor output voltage and sets DTC P0137 or P0157 . During active air-fuel ratio control, if the target ratio is lean but the output voltage is greater than 0.59 V (rich), the ECM considers this to be an excessively high sensor output voltage and sets DTC P0138 or P0158.
If replacing the sensor did not bring results, then the technicians could have replaced the wrong sensor (this happens often), or the problem is not in the sensor, but in the circuit or in an exhaust gas leak. Check all connectors; they may have oxidized or moisture may have gotten into them. Visually inspect the wiring to see if its integrity is damaged. If the circuit is visually in order, then check its operation using an oscilloscope.
Catalog number 1 of the oxygen sensor installed before the catalyst.
“TRC OFF” light on Toyota: How to solve the problem with traction control
Car owners often notice that the “TRC On” light is on. This is traction control. What this feature protects against and controls on modern cars, as well as what to do if “TRC Off” lights up, the reader will find in this article.
The traction control system first appeared in 1971 in America on such famous cars as Cadillac and Buick. It began to be used on luxury cars of the German brand Mercedes since 1987. After the 2000s, manufacturers began to include TRC in every car.
What is TRC
Many car owners notice that the “TRC On” light comes on on various Toyota modifications. But not everyone knows what it is.
TRC translated from English means “Traction Control”. Speed sensors monitor wheel speed and the system uses measures to reduce traction. The first modifications of cars reduced traction by reducing engine speed. Modern vehicles reduce speed using a special viscous coupling.
If the “TRC On” lamp is on, this means that the wheel slip and skid control system is turned on. In Toyota, this system monitors and mitigates skidding and slipping. Although it was originally created only as anti-skid.
The TRC system works as follows:
Thus, traction control protects the driver and the car from creating emergency situations on the roads.
Attention! On cars of the Toyota Avensis, Auris and many other brands, there is a button on the dashboard called “ TRC Off ”. It allows you to disable traction control.
How to use the traction control system
Traction control works when sliding slightly and even where you need to drive a difficult section of sandy road off-road. To drive on country roads, manufacturers have placed a button on the dashboard that turns off the traction control.
By clicking on it, the car owner will be able to drive the car along difficult sections of the road where intensive acceleration of the car is needed, and not blocking the wheels. But drivers should be aware that after pressing the button for a while, it automatically turns off and the traction control system comes into action again. Therefore, it will have to be pressed several times if the car crosses long, difficult sections.
But it happens that the VSC and TRC lamp turn on together on the dashboard monitor. This indicates an error in the driver safety monitoring system.
Other errors detected during diagnostics
When checking the condition of Toyota Corolla systems, other problems may be identified regarding the condition of the power steering, electrical systems, airbags, climate control and other structural elements. Most often, owners encounter the following cases:
- Error P0351 or P0353. These malfunctions are due to the fact that during engine operation the IGF signal is not received by the ECM system. The problem with code P0353 should be looked for in the ignition system. First, it is checked for short circuits, then coils 1–4 are inspected and, if the diagnostics do not reveal problems in these elements, and error P0351 or P0353 does not disappear, the ECM is replaced.
- Code P0136 indicates that the oxygen sensor is faulty: the signal does not exceed 0.55 V when the car is moving at a speed of more than 40 km/h, the engine is warming up to a temperature above 40 degrees Celsius and at a speed level of more than 1400. The problem is why code P0136 may appear , consists of a break in the electrical circuit or a malfunction of the sensor itself.
- Error P0500, indicating damage to the vehicle speed sensor. The instrument fault signal P0500 may come on in the cruise control state and the current signal is interrupted for 0.14 s longer. When P0500 appears, it is necessary to check the electrical system for a short circuit. If the problem is not a failure, and error P0500 has not disappeared, it is worth scanning the instrument panel, the speed sensor itself, the ECU of the anti-skid mechanism and the body. P0500 is an error that is reset after replacing the sensor or electrical components.
- P0133. The code indicates low performance of the oxygen sensor circuit in row 1. The cause of the problem may be a short circuit, a problem with the air intake system, incorrect pressure levels, or a faulty or clogged injector. In addition, the malfunction may be that the sensor itself has burned out.
- Code P2196 indicates a continuous supply of an excessively rich mixture. You should check the oxygen sensor, EFI relay, sensor heater and circuits, and if the problem is not caused by failure of these devices, the cause is the condition of the ECM.
In addition, when diagnosing a Toyota Corolla, you may encounter code P0115: it indicates a malfunction of the cooling fluid temperature sensor (error 22). Also, some owners are faced with the ECU data bus being disconnected: this problem is designated as error 94, and its cause is a malfunction in the CAN system. For the Corolla E120 model, it is not uncommon to receive an error about a malfunction of the protection system: you should check the airbags and make sure that the connectors under the seats are not disconnected.
The car's steering wheel, power steering, Airbag system, or battery may be faulty. A red signal on the dashboard indicates a problem with the corresponding system, and the car may turn on the check and stall: this is especially true if there are problems with electrical systems in cold weather. In this case, it is worth checking the battery charge and sequentially diagnosing various parts of the wiring: the error can most often pop up due to a short circuit.