The owner of the vehicle can perform this procedure independently without the involvement of third-party specialists. To do this you will need a special scanning device. If there is no such desire, then a car repair shop will help to identify the problem.
What does error P 2646 mean?
Modern cars cannot be equipped without electronic sensors that transmit fault data to the electronic control unit (ECU). Based on the data received, an error code is generated and sent to the scanning device.
One of the common Toyota RAV 4 errors is code P2646.
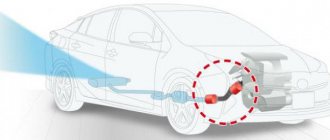
It indicates incorrect operation of the valve drive lever control system. In other words, error P2646 makes it clear to the driver that the VTEC sensor does not produce a signal about the presence of pressure, and the valve opens. There are two reasons for this behavior of the valve lever:
In this case, the sensor contacts are checked: in the normal state they close the circuit, and when pressure is applied to more than 3 atmospheres, the contacts open.
How do I reset the error?
When the diagnosis is completed, the fault must be erased. To do this you need to follow the following direction:
There is a way to reset the block memory using technical means. For example, a computer (laptop) or smartphone. They should be installed with a special application or program designed to remove “extra” information.
Not all drivers have encountered the problem of error P2646. If you have no experience, it is better to contact reliable specialists; they will quickly resolve the issue. If you have the equipment and confidence in your own abilities, you can do everything yourself.
Error codes for Toyota cars - engine, automatic transmission, SRS, ABS and 4WS
A modern car is equipped with a large number of electronic sensors that monitor the correct operation of various systems. If a malfunction is detected, they send relevant information to the electronic engine control unit. It stores a specific error or fault code, which can be read during diagnostics. If the breakdown is serious, the Check Engine indicator lights up on the instrument panel. Thanks to this, the driver can correct the problem in a timely manner. In this article we will look at the most common error codes for Toyota cars. You will also learn how to perform diagnostics yourself.
What to do if Rav 4 error appears
Rav 4
Failures and incorrect operation of vehicle systems are recorded in control units. Toyota cars are no exception. To determine the severity of the problem and identify Rav 4 errors, it is worth conducting self-diagnosis of the systems . This procedure can be carried out by the car enthusiast independently .
Car scanners will make diagnostics easier and more accurate, allowing you to identify error codes that prevent the car from working properly.
Location and types of diagnostic connectors
Cars of the Japanese manufacturer Toyota were equipped with two types of connectors that allow diagnostics - DLC1 and DLC2. More modern models use a DLC3 connector (standard OBD-II).
DLC1 is made in the form of a rectangle located on the left side of the engine compartment (in most cars of this brand). The plastic cover of this connector is marked Diagnostic.
Toyota errors can manifest themselves as follows:
The DLC2 diagnostic connector in almost all cars of this manufacturer is located under the dashboard on the driver's side. Outwardly it differs from the first one. One of the features of this connector is the ability to diagnose a car on the go.
In earlier Toyota models, the diagnostic connector is located in the engine compartment. Typically, it is round in shape and yellow in color. It can often be found near the battery.
Salon and mileage
It’s sad to look at the Toyota Rav4 interior after 100,000 km. The interior materials are for the most part downright cheap. Even after 50,000 km, the steering wheel is already fairly worn out, the side of the driver’s seat is pressed through, and the foam rubber of the seat cushion is slowly starting to crumble.
A few photos from pre-purchase inspections of used cars:
Leather driver's seat cushion. 50,000 km
The back of the leather driver's seat. 50,000 km
As you can see, a fabric seat holds up better over the years.
Steering wheel after 100,000 km
Automatic transmission selector handle. 70,000 km
Crickets from the center console are also not long in coming. All this must be taken into account when determining mileage using indirect signs, since there is no other way - mileage is not recorded in any of the control units, even diagnostics with a dealer scanner are useless in this regard. Only experience and intuition will help.
Self-diagnosis - step-by-step instructions
Professional car diagnostics at a specialized service center is not cheap. In addition, many car owners simply do not have the opportunity to use such services, since they live far outside large cities, and they have no desire to turn to “garage” specialists.
In such cases, self-diagnosis methods come to the rescue. Only basic skills are needed, so even beginners can figure it out. For example, to check engine operation, the procedure is performed in the following order:
If your car uses a DLC3 connector, you need to close contacts TC and CG.
Error codes for the SRS security system in Toyota cars
The codes are read with the ignition on based on the number of times the SRS lamp lights up. In connector DLC1, contacts TC and E1 must be closed, and in DLC3, a jumper is installed between pins TC and CG.
Error codes must be erased when the ignition is turned off. If the codes are stored in memory, follow these steps:
Car scanners
It's easy to get lost among the variety of scanning devices.
To diagnose Rav 4 error codes, both hardware types of devices and scanners from the adapter are used.
Scan Tool Pro is one of them. This instrument is easy to operate and suitable for initial analysis. The scanner is universal . Connects to any type of device running on operating systems such as iOS, Android, Windows, via the standard OBDII protocol .
Pros of Scan Tool Pro:
- compactness,
- versatility,
- ability to save and print out error codes,
- Compatible with Rav 4.
The device detects most faults. And yet, the scanner has one serious drawback - there are too many fake devices on the market. It will be difficult for an amateur to distinguish the original from the fake.
Launch CReader V+ is already equipped with a bright LCD screen and does not require additional connection to devices. The test results are displayed on the screen in the form of text and graphic blocks reflecting the dependence of the values.
Advantages of Launch CReader V+:
- absolute autonomy;
- displaying indicators online;
- long service life;
- ease of operation.
The device has one drawback - the screen is too small .
Delphi DS150E is the leader among affordable automotive scanners. The device is universal and works using the Generic OBD or eOBD protocols , and also scans the available car units. When performing dynamic scanning, data is transferred to a memory card, which is installed in a special slot.
The Delphi DS150E has many features for an affordable automotive scanner, often used in service stations. Some users consider the too large size of the device to be a disadvantage.
Errors in the 4WS system
To read errors, you need to count the number of flashes of the 4WS lamp. In this case, the ignition must be turned on, and contacts TC and E1 in connector DLC1 must be closed.
Decoding the main errors:
Help from our specialists
Dear users of the Autofakty project! Unfortunately, it is extremely difficult to list all Toyota error codes and their detailed decoding. Therefore, if you were unable to find the answer to your question in our article, write to us in the comments at the bottom of the article. Please indicate the year of manufacture, car model, engine and gearbox type, as well as the error code for which you are looking for decoding. We will do our best to find an answer to your question as quickly as possible. Stay with us!
CVT survivability
Toyota workers increasingly continue to combine their creations with lightweight and economical Aisin CVTs. The K111F model was already installed on the previous generation Toyota RAV4 and has earned a good reputation, or more precisely, this CVT belongs to the caste of one of the most reliable.
The CVT can only be seen on 2-liter models. Previously, you shouldn’t worry about 200 tkm, but with proper care, that is, without overheating and timely oil changes, it can last all 300 tkm. Cases of breakdowns at 50 tkm also happen and, fortunately, are very rare.
The Aisin K111F variator belongs to the caste of some of the most reliable
You can find out about the weak points of the U760F automatic transmission, which works with a 2.5-liter unit, in our Toyota Camry review. I will only say that under the hood of the Rav4 such a gearbox works with no less devotion and dedication, allowing 300 tkm to be driven without serious incidents, but again subject to periodic oil changes.
Periodic oil changes in the automatic transmission will be mandatory if you are going to drive the car indefinitely.
The diesel engine received one of the most problematic gearboxes - Aisin U660F, known from the Camry sedan with 3.5. It’s just that under the hood of the Rav4, the automatic transmission, surprisingly, behaves more compliantly, even despite the fact that the torque of the heavy fuel 2.2 is similar to the gasoline 3.5, and the car’s weight is greater. Probably, low diesel speeds reduce the risk of “frying” the clutches and less wear products are formed.
With all-wheel drive there are no problems here. Even if you want to find fault with something, you can mention the tendency to blow snot through the seals of the rear gearbox. And in search of truly weak points, you need to look lower, that is, the chassis and steering.
Decoding error codes on Toyota cars
Technical defects appear sooner or later in cars of all manufacturers, including Japanese ones. The driver can decipher Toyota error codes independently, and it is possible to determine system malfunctions without the use of scanners. If a car enthusiast has never encountered such a problem before, then this article will help you understand all the nuances and perform the work at a professional level.
How to Troubleshoot or Reset Trouble Code P2646
Some suggested steps to troubleshoot and fix error code P2646:
- Read all data and error codes stored in the PCM memory using an OBD-II scanner.
- Reset the stored codes and test drive the car.
- If error P2646 returns, check the connectors and wiring for damage or poor contact.
- Check the rocker arm drive as well as the rocker arm itself.
- Check the level, quality, and pressure of the engine oil.
- Test the VVT/VTEC pressure switch.
- If the code is still active, the PCM will most likely need to be flashed or replaced.
Toyota car diagnostics
Diagnostics are available on cars of the entire Toyota model range and are divided into two types:
Before starting electronic diagnostics, the driver must ensure that all systems and main mechanisms of the Toyota vehicle are in working order. To do this, you should check the fuses, electrical wiring, and also examine the connections and components of the vehicle for damage.
If any serious problem is detected, it must be eliminated, and only then carry out computer diagnostics, which can happen:
Step-by-step self-diagnosis
For self-diagnosis, the driver needs to work with the DLC 1 and DLC 2 connectors. This abbreviation stands for Data Link Connector, which in English means a connector for connecting data. DLC 1 looks like a plastic box with a lid on top. It is located under the hood, most often on the left. It is easy to find by the inscription Diagnostic.
Diagnostic signature on the connector
In older models, the diagnostic connector is shaped like a yellow circle and is located near the battery. There are no DLC2 parts in cars like the Corolla AE 100.
Fault codes for older car models: Toyota Corona 1992, Karina 1992-97, Toyota Mark are read only by flashing indicators.
In new models, DLC 2 is located directly in the cabin, under the dashboard and “at the feet” near the steering wheel. Most often it is round and is used during inspections carried out using special equipment.
Round DLC2 connector
When performing self-diagnosis by shorting individual contacts of the connector, only by connecting them in the required sequence can you obtain the correct code for decoding.
The following steps will help you find out if there are faults in the engine and/or gearbox system:
DLC 1 connector diagram
Everything is fine with the car and no damage to the internal combustion engine or transmission was detected if:
Any other combinations of light bulbs indicate a malfunction in the engine systems, gearbox or other mechanisms in the car.
If the circuit on the back of the cover has been erased, you cannot find the contact or you are not sure that you have closed the right one, you must:
It will be more convenient if someone helps you monitor the light bulb while you change the position of the wire.
Recognize fault codes using two flashing light systems.
The first setting option will allow you to find out errors indicated by a two-digit code (type 09):
Using the 10th setting type, unambiguous codes are determined. Here the light “blinks” the exact error number.
This code should be “read” according to the following rules:
The video shows diagnostics using type 9 code, author Dmitry Kuzmin:
Failures in the ABS system are determined using the same scheme, but the TC and E1 terminals are closed. The SRS and 4WS fault codes are read by the corresponding sensor with the same contacts closed as in the ABS.
Photo gallery “Self-diagnosis of Toyota cars”
Diagnostic connector DLC 1
Contacts TE1 and E1 on the connector
Closing contacts
Location of the connector under the hood
Diagnosis and problem solving
Before you begin the P2770 troubleshooting process, you should review the technical service bulletins (TSBs) for your specific vehicle. In some cases, this can save a lot of time by pointing you in the right direction.
Next, you need to check the fluid level and check its condition for contamination. Before changing the fluid, you should check the vehicle's records to see when the filter and fluid were last changed.
After this, a detailed visual inspection should be carried out to check the condition of the wiring for obvious defects. Check the connectors and wiring to the torque converter solenoid valve and the PCM or TCM.
Normal readings for wiring and connections should be 0 ohms resistance. Wiring continuity testing should always be performed with power removed from the circuit. To avoid short circuit and causing further damage.
Resistance or lack of continuity indicates faulty wiring that is open or shorted. In this case, repair or replacement will be required.
Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Solenoid
Check the resistance in the TCC solenoid and internal transmission wiring after removing the harness connector. The multimeter should be set to ohm scale with positive and negative terminals on the power and TCC control circuits.
Resistance must be within manufacturer specifications. If it is very high or exceeded. Remove the transmission oil pan to inspect the solenoid inside the transmission, if possible. Check voltage at the TCC solenoid power circuit or at the harness connector at the TCM.
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
Because the torque converter clutch is only activated during certain driving conditions. The TCM will need to be monitored using an advanced scan tool. To determine if the TCM is commanding the TCC solenoid and what the actual feedback reading is.
To check if the TCM is actually sending a signal, you will need a graphical multimeter set to duty cycle or a digital storage oscilloscope. We connect the positive lead of the multimeter to the wiring harness going to the TCM. And the negative wire to a good ground.
The duty cycle should be the same as that specified by the TCM in the scan tool's extended reading. If the cycle remains at 0% or 100% or is intermittent, check the connections again. If all wiring and solenoid are good, but the P2770 code remains, the TCM may be faulty.
Troubleshooting
Type 9 error codes common to all Toyota vehicles are represented by two-digit codes.
| Code | Decoding |
| 11 | No power to EFI unit |
| 12 | No signal from the engine speed sensor |
| 13 | No signal from the engine speed sensor at speeds above 1000 rpm |
| 14 | There is no signal from the minus ignition coil or from the minus coil number one (if there are two of them) |
| 15 | There is no signal from the minus of ignition coil number two |
| 16 | There is no connection between the automatic transmission control unit and the engine control unit |
| 17 | Incorrect signal from camshaft position sensor number 1 |
| 18 | Incorrect signal from camshaft position sensor number 2 |
| 21 | Incorrect signal from the oxygen sensor, if the engine is V-shaped, then the heater of the left main oxygen sensor is faulty |
| 22 | Incorrect signal from engine temperature sensor (THW) |
| 23 | Incorrect signal from the intake air temperature (THA) sensor |
| 24 | Incorrect signal from the intake air temperature (THA) sensor |
| 25 | Mixture too lean |
| 26 | Mixture too rich |
| 27 | Incorrect signal from the additional oxygen sensor (left for V-engines) |
| 28 | Incorrect signal from the oxygen sensor (on V-engines, the heater of the right main oxygen sensor) |
| 29 | The additional oxygen sensor is faulty (right for V-engines) |
| 31 | Incorrect signal from the air flow sensor or, if there is none, from the pressure sensor in the intake manifold (vacuum sensor) |
| 32 | Incorrect signal from air flow sensor |
| 34 | Boost faulty |
| 35 | Incorrect signal from the atmospheric pressure sensor in the intake manifold (vacuum sensor) |
| 38 | Automatic transmission fluid temperature sensor |
| 41 | Incorrect signal from throttle position sensor (TPS) |
| 42 | Incorrect signal from the vehicle speed sensor (speedometer) |
| 43 | No starter signal (STA) to engine control unit |
| 46 | Solenoid valve number 4 or its circuits are faulty |
| 47 | The auxiliary throttle position sensor (TPS) or its circuit is faulty |
| 48 | The auxiliary air supply control system is faulty |
| 51 | No idle signal from TPS |
| 52 | Incorrect signal from the knock sensor (if there are two of them, then from the left or from the front) |
| 53 | Problems in knock sensor control circuits (ignition timing) |
| 55 | Incorrect signal from the knock sensor (if there are two of them, then from the right or from the rear) |
| 61 | The main speed sensor or its circuit is faulty |
| 62 | Solenoid valve number 1 or its circuits are faulty |
| 63 | Solenoid valve number 2 or its circuits are faulty |
| 64 | Solenoid valve number 3 or its circuits are faulty |
| 65 | Solenoid valve number 4 or its circuits are faulty |
| 67 | The O/D switch or its circuit is faulty |
| 71 | EGR control system faulty |
| 72 | Fuel cut solenoid |
| 77 | The pressure control solenoid or its circuit is faulty (in the machine) |
| 78 | There is no signal to the fuel pump or its circuits are faulty |
| 81 | The circuit between TCM and ECT1 is faulty |
| 82 | The circuit between TCM and ESA1 is faulty |
| 84 | The circuit between TCM and ESA2 is faulty |
| 85 | The circuit between TCM and ESA3 is faulty |
| 86 | Engine speed sensor is faulty |
| 88 | The circuit from the engine control unit to the automatic transmission control unit is faulty |
| 89 | Communication between the engine control unit and the TRC system control unit is broken |
| 99 | No fault codes |
The general list of unambiguous codes (type 10) for a Toyota car consists of the following items.
| Code | Decoding |
| 1 | No breakdowns |
| 2 | The air flow sensor gives an incorrect signal |
| 3 | Incorrect signal from the communicator |
| 4 | The coolant temperature is outside the normal range, the sensor has failed |
| 5 | Incorrect communication with the oxygen sensor |
| 6 | The fault lies in the number of engine revolutions |
| 7 | Throttle valve in incorrect position |
| 8 | The sensor shows incorrect intake air temperature |
| 9 | Car speed problem |
| 10 | There is no starter signal |
| 11 | The air conditioner is broken or the toggle switch responsible for the neutral position in the car is faulty |
Gasoline internal combustion engines
If the car has an on-board computer or robot, the code will appear on the mileage screen. It will consist of a Latin letter at the beginning, for example P, B, C, and 4 numbers. This is typical for cars such as Toyota Rav 4 Avensis, Corolla, Mark II or Land Cruiser 200, Toyota Prado 120 and others that run on gasoline.
Table for deciphering diagnostic fault codes for gasoline internal combustion engines.
| Codes | Decoding | Analogue on BC |
| 12 and 13 | Problems with the crankshaft position sensor | P0335, P0335, P1335 |
| 14 and 15 | Problems with the ignition system or coils | P1300 and P1315, P1305 and P1310 |
| 18 | VVT-i phase system | P1346 |
| 19 | Accelerator pedal position | P1120 and P1121 |
| 21 | Oxygen sensor | P0135 |
| 22 | Coolant temperature | P0115 |
| 24 | Damage to the intake air temperature sensor | P0110 |
| 25 | Oxygen sensor - lean mixture | P0171 |
| 31 | Absolute pressure sensor | P0105 and P0106 |
| 36 | CPS sensor | P1105 |
| 39 | VVT-i system | P1656 |
| 41 | Throttle position | P0120, P0121 |
| 42 | Vehicle speed sensor problems | P0500 |
| 49 | Fuel pressure D-4 | P0190, P0191 |
| 52 and 55 | Knock sensor failure | P0325 |
| 58 | SCV drive | P1415, P1416, P1653 |
| 59 | Incorrect VVT-i signal | P1349 |
| 71 | EGR system | P0401, P0403 |
| 89 | ETCS drive | P1125, P1126, P1127, P1128, P1129, P1633 |
| 92 | Cold start injector problems | P1210 |
| 97 | Injector faulty | P1215 |
Diesel engines
Many Toyota cars were produced with a diesel engine. The most popular models are the Vitz, Caldina, Avensis (T25), Camry, Camry Grazia, Corolla E150, Auris 2008 sedans, Land Cruiser Prado 120 and Land Cruiser Prado 200 SUVs or the RAV4 crossover.
When writing down codes for diesel cars, you can see the following symbols.
| Code | Decoding |
| 13 | Rotation speed is outside the permissible limits |
| 19 | Incorrect accelerator pedal position |
| 22 | Malfunction in coolant temperature indicators |
| 24 | Incorrect intake air temperature data |
| 35 | Boost pressure is out of range |
| 39 | Fuel temperature sensors do not work well |
| 42 | The fault lies in the vehicle speed sensor |
| 96 | EGR valve position is incorrect |
Failure of other diesel engine parts.
| Code | Decoding |
| 12 | Crankshaft position problem |
| 14 | Damage to the valve that regulates the injection advance angle |
| 15 | The throttle servo is faulty |
| 17 | Incorrect signal coming from the control unit |
| 18 | Damage to the solenoid bypass valve |
| 32 | Failure of correction resistors |
Automatic transmission
Cars of the same brand differ not only in the engine, but also in the gearbox. For the same Toyota Corolla 150, Celsior or Vista, automatic transmission failures will differ from mechanical failures.
If there is a malfunction in the transmission, you will see one of the codes.
| Code | Decoding | Analogue for automatic transmission |
| 37 | Transmission input shaft speed sensor malfunction | P1705 |
| 42, 44, 36 | The problem is in the speed sensor (maybe shaft speed) | P0500 |
| 46 | Accumulator pressure, solenoid faulty | P1765 |
| 62, 63 | Problems with one of the solenoids | P0753 P0758 |
| 64, 68 | Torque converter lock-up clutch, solenoid faulty | P0773 |
Such errors are typical for different models, including Toyota Ipsum, Toyota Highlander 2001 and Caldina.
Other combinations
Special equipment and devices are also used for diagnostics. Such devices will show five-digit codes. They can also be recognized using the on-board computer, which is installed in new cars and hybrid models.
Code on the Toyota screen with on-board computer
Toyota Estima, Toyota Prius, third generation Toyota Harrier and others came out in the hybrid version. These models (in addition to other breakdowns) may experience malfunctions of the high-voltage battery system (HVB). Hybrid installation error codes and their interpretations are given in the table.
The most common non-VVB error codes are:
| Code | Decoding |
| P1604 | Engine starting failed, failure in the intake system |
| B0101 | The security system does not work correctly, there are problems with the airbags |
| In 1801 | The squib circuits on the driver's side are broken. |
| C1201 | Engine operation is incorrect, speed is below the permissible level |
| P0420 | Catalyst system B1 operates below the permissible efficiency threshold |
| P0352З | Problems in the ignition system circuits |
The photo gallery shows errors in the operation of the immobilizer and tires on Toyota cars.