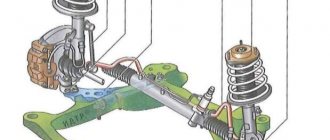
Suspension in a car is a suspension system that dampens shocks that occur when driving on uneven roads. The front and rear suspensions together with the wheels form the chassis of the car. The suspension is a complex assembly consisting of guides, elastic, shock-absorbing elements and fastening elements. Mechanical elements are combined with pneumatic, hydraulic, and electrical ones. One car can use different types of front and rear suspensions. So, the front suspension of the Toyota Corolla is independent, MacPherson type, and the rear is semi-independent, like a torsion beam.
Suspension functions
Suspension is the connecting link between the wheels and the main supporting system of the car - the frame and body. This unit provides a movable, not too rigid connection between the wheels and the body, in which they move up and down relative to the frame and body of the car. By ensuring vertical movement of the wheels, the suspension simultaneously limits their lateral and angular movements, which deteriorate the stability of the car. If it were not for the suspension, any shock from the contact of the wheels with the road would be fully transmitted to the body, and the car, instead of bouncing on bumps, would wobble left and right. The suspension solves the following problems:
- due to the connection of moving and fixed elements, it ensures vehicle movement, acceleration and braking, turning and lateral maneuvers;
- increases vehicle stability and improves handling, ensures a smooth ride, prevents skidding and rollovers;
- stabilizes the position of the car when turning;
- absorbs shock energy, protects body parts from premature wear and makes the ride more comfortable for the driver and passengers.
There are no diamonds in a car suspension, but for a car this unit is priceless
Actions if there is a knock
If extraneous sounds appear while driving, you should determine the source of the knock. Sometimes noise occurs due to poorly stowed tools in the trunk or rolling cargo. If the source of the knock is not detected, then the functionality of the suspension parts should be checked. Small stones that have fallen on the lever or the metal protection of the engine crankcase can make a knocking sound. Sometimes noise is caused by a poorly secured muffler. It is not recommended to operate the car until the cause of the knocking is identified and subsequent repairs are made.
Types of pendants
Suspensions predate the invention of automobiles. The prototype of modern automobile suspensions can be considered the suspension system of carriages - their interior was suspended on leather belts or chains. But this design dampened shocks only at low speeds. In 1804, Obadiah Elliott patented a suspension on arc-shaped longitudinal springs; the springs were made of steel, or, less commonly, of elastic wood. Improved suspensions of this type were widely used in cars from the moment they appeared until the 70s of the last century, and are still found on some models today.
The suspensions that were used in different eras on different types of transport differed from each other in their design features. The guiding elements were longitudinal or transverse springs or levers. The elastic elements were springs, springs, torsion bars, rubber blocks, pneumatic cylinders, and hydropneumatic elements. Over more than 2 centuries, dozens of design variations of this unit have appeared. The most common is the division of suspensions according to the type of connection between wheels located on the same axis. According to this principle they are divided into:
- dependent;
- independent;
- semi-dependent.
The dependent suspension rigidly connects the wheels through a continuous beam, so the left and right wheels are always mutually parallel. The disadvantages of this design appear when traveling on uneven roads: when one wheel hits an obstacle, both bend. The main advantage of dependent suspension is its simplicity of design and low price. Motorists half-jokingly say that independent suspension is more convenient as long as it does not need to be repaired. Nowadays, front dependent suspensions are not used on passenger cars, with the exception of some SUVs, and rear suspensions are installed mainly on budget front-wheel drive cars.
In an independent suspension, the wheels are not rigidly connected and move independently from each other; the right and left wheels have their own vibration damping system. They can be connected by swinging axle shafts, a system of longitudinal, transverse or oblique levers. Models with double wishbones may use additional control arms, called a multi-link design. Due to the complexity of the design, the production and maintenance of a multi-link suspension is more expensive than other types, but it provides the most comfortable control.
For cross-country trips, a simplified type of independent suspension is preferable - McPherson (McPherson, floating spark plug). It is this system that is used as the front suspension of the Toyota Corolla. In MacPherson strut suspension, the shock absorber strut consists of a spring and a telescopic shock absorber. The upper part of the shock absorber is attached to the body by an elastic hinge, which allows it to swing. The principle of operation of a suspension with a shock absorber strut is clearly shown in the video.
A semi-independent suspension is cheaper than an independent one, is easier to maintain and provides a smoother ride and improved handling compared to a dependent one. The rear suspension in front-wheel drive cars is often semi-independent, the most common type being a torsion beam. The beam itself, connecting the wheels, is rigid, but it is attached to the body by means of elastic elements - torsion bars. A torsion bar is a rod that twists when the suspension arm moves. When one of the wheels of the axle hits a small obstacle, its vibrations are not transmitted to the second wheel. But if the irregularities are significant, the range of vibrations of the wheel increases and the presence of a connection between the wheels still makes itself felt.
In general, about the maintenance of the Toyota Fielder chassis
The chassis of the Toyota Corolla Fielder is quite good in maintenance. There are quite a lot of spare parts on the market, they are not very expensive and most importantly, they are all quite easy to change. For example, replacing stabilizer links or springs is a very simple process. But for many motorists who do not understand cars, they will need step-by-step instructions that will help them figure it out and make all the repairs themselves. Replacing rods or ball joints is not a problem at all. Changing silent blocks - as we have already seen ourselves, generally takes 5 minutes.
When buying a Toyota Corolla car, you should know that they are highly reliable, especially the engine and chassis of the car perform well. As for ergonomics and comfort, the Japanese, as always, are at their best.
Suspension elements
There are three main groups of suspension elements:
- guides and connectors - levers that connect the wheels to the body and ensure their movement relative to each other;
- elastic - in Toyota Corolla these include springs that evenly distribute the load from road unevenness onto the body;
- damping (damping) shock absorbers dampen vibrations of the body that occur when a load is transferred to it by elastic elements.
The suspension design also includes:
- steering knuckles;
- wheel hubs with brake discs;
- anti-roll bar;
- stretcher;
- fastening elements - silent blocks, ball joints or supports, bolted connections, brackets.
The unit connecting the wheels of one axle is called a bridge. For independent suspension it is split, for dependent and semi-independent suspension it is continuous, made in the form of a hollow beam.
Purpose of elements
By means of a subframe, the suspension is connected to the body, and a number of elements of the suspension itself are attached to it, in particular, levers. A suspension arm is a cast or stamped metal part that allows the wheel to move up and down, but limits its longitudinal and lateral movements. This is the connecting link between the suspension subframe and the wheel. But it is not directly connected to the wheel. The lever is attached to the subframe at one end, and to the steering knuckle at the other.
The steering knuckle is responsible for turning the car, it is the connecting link between the chassis and the steering, and the steering rods are attached to it. The wheel hub is also inserted into it. The steering knuckle transmits the force that is applied when rotating the steering wheel to the suspension elements, and the hub, through bearings, ensures rotation of the wheel. The braking force is also transmitted to the hub via the brake disc. The disc can be installed on the hub or be integral with it.
The most important element of the suspension is the shock-absorbing strut, which combines elastic and damping elements. In a McPherson strut, the shock absorber is located inside the spring, and this assembly also includes a number of auxiliary parts:
- spring seat;
- support and cap securing it;
- upper and lower insulators;
- rubber damper and dust ring.
An elastic rod is connected to the levers through the struts - the anti-roll bar. It limits the car's sway and reduces its roll when cornering.
There is such a thing as hard or soft suspension. The more the elastic element is able to compress and stretch and the more intense the shock absorber absorbs vibrations, the softer the suspension. A rigid suspension softens shocks less well, but better ensures stability of the car when cornering. Soft makes the ride more comfortable, but to a certain limit. A car with too soft a suspension not only sways a lot when maneuvering, the amplitude of body vibrations when driving in a straight line also increases. Rocking due to an overly soft suspension is just as unpleasant as shaking due to a very hard one. So manufacturers strive to find the ideal balance of softness and hardness.
A soft suspension increases comfort but worsens handling, while a hard suspension does the opposite.
Fastening elements provide connection of functional suspension elements to each other and fastening of the subframe to the body. A silent block is a hinge made of metal bushings, between which there is an elastic rubber or polyurethane insert. Its main purpose is to connect nodes and dampen vibrations when transmitting forces between them. In the suspension, it serves to attach the arms and anti-roll bar. Ball joints provide a movable articulated connection between the arms and the steering knuckles. Anthers protect them from contamination. Auxiliary suspension elements also include bushings and rubber mounting pads.
Weak points of the suspension
To diagnose the suspension you need an inspection hole or at least a jack
It is the connecting elements that are subject to the greatest load and most often need to be replaced. So, if you hear a knock from the front suspension of a Toyota Corolla or it makes a creaking noise on bumps, the reason may lie in the wear of the strut parts or connecting elements. Among the contract spare parts for Toyota Corolla suspension, struts are the most in demand. The shock absorber strut assembly can be changed, but more often the shock absorbers wear out when the spring life has not yet been exhausted. The front suspension shock absorbers need to be changed in pairs, and at the same time consumables are changed - anthers, dampers (bump stops), bushings, spring pads.
Wear-out rubber elements must be replaced with new ones, as well as bolts and nuts with broken threads. If diagnostics of the Toyota Corolla suspension showed that the shock absorber has failed, the strut spring has burst or sagged, the rods of the levers, the stabilizer, the stabilizer bar itself, the beam have become deformed, you can use contract spare parts to repair the Toyota suspension.
According to reviews from car owners, the rear and front suspensions of the Toyota Corolla, due to the simplicity of their design, are very reliable, even on Russian roads they are difficult to kill. Shock absorbers can withstand up to 100 thousand kilometers, wheel bearings - up to 150 thousand, silent blocks and ball joints - up to 200 thousand. But the bushings and bearings of the front struts need to be replaced more often. Other elements wear out slightly, except that they may become deformed in an accident.
What should I do?
The Corolla 150 and 120 are durable and reliable cars, but they do not last forever, so to extend the life of your car, you need to pay attention to it. It is recommended to promptly change consumable parts such as stabilizers: thanks to them, the car holds the road better and maneuvers without skidding. As a rule, they need to be changed at around 80 thousand mileage. You can replace them yourself if you have a car design diagram.
It wouldn't hurt to replace the silent blocks along with the stabilizers. Every 150 thousand km it is recommended to change the ball joints.
Replacement 120-150 body
When everything necessary for the work is prepared, you can start replacing;
- First of all, the car is driven into a pit, this will allow you to gain access to the necessary components;
- The car is lifted with a jack;
- The lever is dismantled; to do this, the ball is disconnected from it and the through bolt of the front silent block and the rear bracket are removed; if you can’t unscrew the bolt, you can cut it off with a grinder;
- Using a puller, a silent block appears from the lever to make removing the part easier; it is advisable to tap it with a hammer and cut it off as much as possible;
- A new silent block is installed, pressing is carried out, this can be done using a vice or any other press. Before installation, it is advisable to clean the surface and apply lubricant;
- The assembled part is mounted back on the car.
Important: To avoid problems with the bolts during the next replacement, they need to be lubricated with a special graphite lubricant, this will help prevent the bolts from boiling. You can find this lubricant in almost any auto store!
Catalog articles for silent blocks
| Name | Article/OEM | Price, rub.) |
| Rear axle silent block | FEBEST TAB166RUB | from 250 |
| Front arm silent block, front | FEBI 19009 | from 350 |
| Rear tie rod bushing | FEBEST TSB803 | from 350 |
| Suspension arm silent block | GSP 516723 | from 350 |
| C. rear link | FEBEST TABAE100CL | from 350 |
| —/— | GSP 510689 | from 350 |
| Bracket, lever cushions | Ashika GOM236 | from 450 |
| Silent block | RUVILLE 986901 | from 450 |
| —/— | FENOX CAB10023 | from 450 |
| —/— | KAVO PARTS SCR9007 | from 450 |
| —/— | FEBEST TAB010 | from 450 |
| —/— Toyota Corolla | YAMATO J42016AYMT | from 450 |
| —/— | FENOX CAB10055 | from 450 |
| -/- rear | FENOX CAB03018 | from 550 |
| —/— | Blue Print ADT38015 | from 550 |
| —/— | FENOX CAB02027 | from 550 |
| -/- rear | YAMATO J42014BYMT | from 550 |
| —/— | FEBEST TAB198 | from 550 |
| —/— | JAPANPARTS RU236 | from 550 |
| -/- rear | DELPHI TD372W | from 550 |
| —/— | JAPANPARTS RU2553 | from 550 |
| -/- rear | FENOX CAB20049 | from 550 |
| —/— | JAPANPARTS RU2454 | from 550 |
| —/— Toyota Corolla | FENOX FSB00040 | from 550 |
| —/— | Blue Print ADT38085 | from 550 |
| —/— | Ashika GOM2553 | from 550 |
| -/- rear | KAVO PARTS SCR9032 | from 550 |
| —/— | Nipparts J4232009 | from 550 |
| -/- rear | JAPANPARTS RU237 | from 550 |
| —/— | FEBEST TAB080 | from 550 |
| -/- rear | MAPCO 33561 | from 550 |
| —/— Toyota Corolla | JAPANPARTS RU267 | from 550 |
| —/— | Optimal F85286 | from 550 |
| —/— | SWAG 81929185 | from 550 |
| -/- rear | SIDEM 845647 | from 550 |
| —/— Toyota Corolla | MOOG TOSB7368 | from 550 |
| —/— Toyota Corolla | RUVILLE 986902 | from 550 |
Choice
The stability of the suspension and the softness of the levers will depend on the quality of the spare parts. Some car owners, instead of the original ones, install polyurethane analogues, which have a longer service life, but their price is an order of magnitude higher.
Original
The original rear silent blocks have the following catalog number: 48068-12300, the price for them is around three thousand rubles.
Analogs
Since the price of original spare parts is relatively high, many car owners choose analogues that cost less. Today their choice is very large, for example:
Important! It is recommended to purchase original silent blocks, since analogues have a much shorter service life.