First mass hybrid
Hybrid car development has been going on since the beginning of the 20th century, but neither Ferdinand Porsche nor Swedish Volvo managed to do what Toyota did, namely create the first mass-produced hybrid car. Toyota Prius lives up to its name in this too. Released in 1997 for the Japanese market, then only a sedan, it quickly conquered the domestic market and began to conquer the world within three years.
Read also: The best paper airplane
Thanks to the low amount of harmful emissions and low fuel consumption, the car became extremely popular in North America, where, due to fashionable trends for “greening”, by 2008 more than half a million cars had been sold, and global sales exceeded a million. As of 2021, the number of hybrids produced and sold has exceeded 10 million units.
Creation
Toyota engineers started thinking about creating the car of the future back in 1993, creating a scientific group called Global21, and outlined the requirements for transport of the 21st century - a long wheelbase, spaciousness in a small size and fuel economy. The initially set goals to reduce fuel consumption by a third were no longer relevant a year later.
A new goal for the research team was the development of a power unit with consumption halved. An option to solve this problem was the development of a hybrid engine (THS) for the Toyota Prius, the decision to release which was approved in 1995.
In the same year, the first Prius was assembled, which the creators could not get moving for almost 2 months. The first “mileage” of the hybrid was only five hundred meters, after which the car went for a two-year revision. The official presentation of the first Toyota Prius coincided with a climate change conference, and it was not a prototype, but a copy of a hybrid that came off the production line. Prius in its first body was greeted with a bang and began a confident march to conquer the automotive world.
Environmental friendliness
In the first decade of Prius production, it had no equal in terms of environmental friendliness and fuel consumption. Over time, many automakers adopted Toyota's experience and presented their own versions of hybrid cars, and also achieved perfection in the production of classic internal combustion engines, reducing their fuel consumption and emissions.
The Toyota Prius' environmental contributions don't stop with its hybrid powertrain. The car is designed in such a way that it contains no toxic materials (for example, PVC), and all plastic is successfully recycled. Recycled materials are also used to make many parts such as hoses and tubes. A specially created network of collection points is engaged in the disposal and further processing of used batteries.
Prius C Specifications
Toyota Prius C is built on the front-wheel drive Toyota B platform. The suspension design is classic - MacPherson strut in front and semi-independent torsion bar at the rear.
Dimensions
The main difference between the younger Prius is its size. Because of them, the hybrid belongs to the compact class (B in the European classification).
Dimensions – 399.5 cm x 169.4 cm x 144.5 cm;
Ground clearance – 14 cm;
Wheelbase – 255 cm;
Weight – 1134 kg.
Aerodynamic drag – 0.28 cW
Small dimensions allow the hatchback to feel comfortable in the city. The maximum turning radius is only 4.8 meters, and the 36-liter fuel tank does not require frequent searching for a gas station to refuel the hybrid. A spacious luggage compartment of 484 liters will allow you to transfer a sufficient amount of cargo, despite the fact that the useful volume of the luggage compartment is not occupied by a spare wheel and the necessary tools located in it. The number of seats in the hybrid is five.
Parameters of the hybrid power unit
Under the hood of the hybrid there is a tandem of gasoline and electric motors.
The first, brand 1NZ-FXE, volume 1.5 liters, has 73 hp. power. The engine is equipped with a VVT-i system. ICE torque is 111 Nm at 4000 rpm. The compression ratio is at the level of diesel engines - 13.4.
Under the hood of the Prius C
The second - with the index 1LM, consists of 20 nickel-hydrogen batteries with a capacity of 6.5 Ah. The power of the hybrid electric motor is 45 kW and torque is 169 Nm.
The coordinated operation of both hybrid engines, coupled with low weight, made it possible to achieve low fuel consumption. In the city it is 4.4 liters, in mixed mode - 4.7 liters. But when driving on the highway, due to prolonged use of the internal combustion engine, consumption increases slightly and amounts to 5.1 liters of AI-95 gasoline per 100 kilometers.
Nothing has changed under the hood of the restyling.
Safety
Toyota cars traditionally have a high level of safety. To successfully pass the tests, the hatchback was slightly modified in 2015: some parts of the body were strengthened, and the side airbags were modified. After this, the Toyota Prius C received a high rating of "Good" in terms of safety. The hybrid is equipped with the following systems:
- anti-lock brake system (ABS);
- electronic brake force distribution (EBD);
- Brake Assist System (BAS);
- exchange rate stability system (ESP);
- traction control system (TCS);
- Hill start assist (HAC).
Interior of the updated Prius C
Safe transportation of children is guaranteed by ISOFIX fastenings and a door locking system while driving.
Do not forget that the hybrid leaves the assembly line with 6 airbags installed on it.
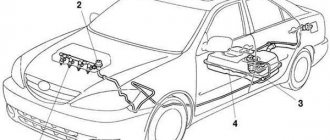
Prius hybrid powertrain
The Toyota Prius engine is a tandem of an internal combustion engine and an electric motor. At the same time, the car requires refueling exclusively with gasoline, and the battery energy is replenished by a generator and a current converter. A design feature of the Toyota Prius is the ability to connect to the drive wheels, both a gasoline and an electric motor. This is implemented as follows: at the start and when driving at low speeds, the car moves on an electric drive.
When the speed and revolutions increase, the initiative is taken over by the internal combustion engine, which, in addition to transmitting energy to the continuously variable transmission, drives the generator pulley, which charges the batteries. During sharp acceleration, both hybrid motors operate, thereby increasing torque to accelerate acceleration. In addition to charging from a gasoline engine, the Toyota Prius is capable of replenishing battery capacity using regenerative braking energy. And when stopping, even for a short period of time, for example, at a traffic light, all power systems are turned off, saving energy.
However, in some modes it is possible to operate a gasoline engine at idle or in slow motion. This occurs when the battery's charge level has dropped and requires recharging. And it can decrease, for example, during a long period of inactivity, so during downtime the Prius must be started at least twice a month.
You will also not be able to use the car if the amount of fuel in the tank is low. The car will “demand” to replenish its supply, despite the battery being fully charged.
Versions and generations
Today, the Toyota Prius lineup consists of four full generations. Each of them underwent a certain kind of modernization or had a submodel.
1st generation XW10
The first hybrid Prius body, released in 1997, was a five-seat sedan. For three years, Toyota has not developed international sales of this car due to the low traction capabilities of the hybrid power unit. A 1NZ-FXE engine with a volume of 1.5 liters and a power of 58 hp was installed as an internal combustion engine. (a little over 42 kWh).
The maximum power of the electric motors was 30 kW*h. This was not enough even for a quiet ride in a car whose weight was 1240 kg. Only in 2000, engineers managed to increase the output of the power plant (up to a total of 86 kWh) and reduce the consumption of the gasoline engine (from 2.9 to 5.9 liters per 100 km, depending on conditions). After this, Toyota Prius began to be actively sold in Europe and North America.
Buyers liked the hybrid's spacious interior, stylish design and absolute silence. The interior was also different from regular Toyotas - the instrument panel was located in the center, near the windshield. The operating status of the hybrid installation could be monitored on a 6-inch screen. It was also used to control the multimedia system. The car was equipped with 2 airbags, and the belts had pretensioners and force limiters.
Read also: Mreo Miass, Chelyabinsk region
2nd generation XW20
The next Toyota Prius hybrid body was produced by a Japanese company from 2003 to 2009. According to representatives of the auto giant, this car was developed “from scratch.”
Externally, the car has changed dramatically, becoming a five-door hatchback. The number of airbags in the car tripled, and the body was made of high-strength steel.
Changes also affected the interior. The steering wheel has become oval, and multimedia control buttons have appeared on it. The screen has increased to 7 inches. Music, a Bluetooth-connected phone, and the air conditioning system could be controlled using voice commands. By the way, the air conditioning and heater were powered by an electric compressor, regardless of the gasoline engine.
The THS II hybrid system was an electric drive increased to 50 kWh, allowing it to reduce the load on the internal combustion engine, thereby saving fuel. The weight of the batteries decreased by 14%, which also had a positive effect on the dynamics of the car. The upgraded 1.5 liter engine also increased its power to 77 hp.
3rd generation XW30
The third generation Toyota Prius has increased slightly in size, while maintaining a recognizable classic design. The tilt of the A-pillars increased visibility, and the shift of the top point of the body back added comfort to passengers in the rear row of seats.
Innovations did not pass by this generation of Toyota Prius - on the roof of the hybrid in the expensive configuration there were solar panels, with the help of which the interior ventilation system worked on hot days. Ultrasonic sensors assisted during parking by turning the steering wheel in the desired position, and a special radar was responsible for the operation of adaptive cruise control.
The 2ZR-FXE petrol engine had 99 hp. and a volume of 1.8 liters, which at high speeds made it possible to reduce the load and reduce fuel consumption by 10%. The electric motor operated at increased voltage up to 650 volts, thereby its output increased by 20%.
4th generation XW50
The latest generation of the Toyota Prius in the XW50 body, despite its futuristic design, retains the proportions of the previous generation. The interior is designed for maximum comfort for the driver and passengers. The huge 9-inch display has built-in navigation and allows you to control multimedia functions intuitively. The projection system on the windshield is made in color and does not require the driver to switch his attention to the dashboard. The steering wheel is covered with special leather that adapts to the air temperature. Toyota Prius is also equipped with a set of systems designed to prevent accidents.
The power plants have also been modernized. Electric motors are now placed in parallel rather than coaxially, which has reduced energy losses by 20%. But the main innovation was the ability to choose between nickel-metal hydride and lithium-ion batteries. The former provide more stable operation at low temperatures, the latter have a higher charging density.
No changes were made to the gasoline power unit, but it became possible to purchase a Toyota Prius in an all-wheel drive version. The drive to the rear wheels was carried out using an electric motor with a power of 5.4 kW, which, in principle, is enough for comfortable control in conditions of bad or snowy roads.
Microvan XW40
In addition to the classic sedan and hatchback body styles, the Toyota Prius was produced as a station wagon. The increased base of the hybrid made it possible to install three rows of seats and increase the number of seats to seven. The microvan was built on the basis of the third generation and had a lithium-ion battery reduced in size. What is noteworthy is that on three continents the car had different names - Prius α in Japan, Prius V in the USA, and for Europe - Prius +.
Toyota Aqua
In 2011, a modification of the Toyota Prius Aqua appeared, the difference between which and the third generation produced at that time was that fuel consumption was reduced from 3.9 to 2.83 liters. This was achieved by reducing the dimensions and weight of the body. For the North American market, the hybrid was supplied under the name Toyota Prius C.
Prius PHV (Prime)
The first generation rechargeable hybrid, produced from 2012 to 2015, could provide a range of up to 20 kilometers at a speed of 80 km/h exclusively on electric motors. Only when the charge level dropped did the gasoline engine turn on. This made it possible to reduce fuel costs by 45% when traveling long distances.
Externally, the PHV hybrid was distinguished by shiny stickers on the rear and front, blue headlights and the presence of a hatch under which the charging connector was located. Changes in the interior were even less noticeable - the monitor displayed the estimated start time of the gasoline engine.
The second generation of the Prius PHV hybrid received an increased power battery, allowing the car to cover 68 kilometers at speeds of up to 135 km/h. The ability to quickly recharge up to 80% in just 20 minutes from a 240 Volt network became innovative.
On the outside, the Prius PHV gets larger grille and bumper elements, as well as two-tone wheels. Instead of a solid sofa, a double seat with a dividing console is installed in the back. Despite the significant advantages of the Toyota Prius PHV, it is not without its disadvantages. Due to the larger battery, we had to sacrifice some of the trunk space. Its volume is only 360 liters, and there was no room for a spare wheel.
Exterior and interior of the updated model
Despite the common name and close relationship, the Prius C is fundamentally different in appearance from the older model. Noteworthy are the hatchback's large air intakes, enlarged front bumper, and at the same time refined radiator grille. The rear of the car is comparable to the front - large lights, a bumper matching them and an equally massive spoiler at the top of the rear door. Looking at the Toyota Prius C from the side, you will notice that the rear angle of the pillars is quite large, which has a positive effect on visibility.
The interior of the hatchback looks stylish. The instrument panel is located in the center, directly above the asymmetrical dashboard. Below is a multimedia display and a triangular-shaped climate control unit.
The Toyota Prius C provides the driver and front passenger with a comfortable seating position due to convenient lateral support and versatile seat adjustments. The second row of the hybrid will also accommodate two passengers without any problems, but three people will be relatively uncomfortable. The quality of plastic materials and all interior trim of the hatchback is at a high level, resistant to abrasion and mechanical damage.
Prius C interior before update