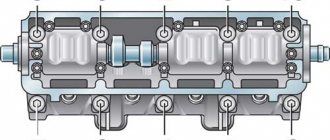
Tightening torque for VAZ cylinder head
Tightening torque of the cylinder head on NIVA Chevrolet engines (VAZ-2123 engine)
Tightening torques of the cylinder head (cylinder head) have the values indicated in table No. 1. The engines that are installed on cars of the Chevrolet Niva family (VAZ-2123) are 4-cylinder, with an in-line vertical arrangement of cylinders and an overhead camshaft. Equipped with a distributed fuel injection system.
The head bolts are tightened in four stages (indicated in the table). And here is what they write about this in the VAZ-2123 operating manual:
Fig. 1 Order of tightening the cylinder head bolts
Install the cylinder head, centering it along the two guide bushings, screw in the bolts securing it and tighten them in four steps in a certain sequence.
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, Nm (kgf*m) |
| Cylinder head bolts | M12x1.25 | 1st - torque 20 Nm (2 kgf*m); 2nd - torque 69.4-85.7 Nm (7.1-8.7 kgf*m); 3rd - tighten the bolts 90°; 4th - finally tighten the bolts 90°. |
| Cylinder head cover bolt | M6 | 1.96-4,60 (0,20-0.47) |
| Cylinder head bolt | M8 | 31,36-39,10(3,20-3,99) |
Table No. 1.
The tightening torque of the cylinder head bolts on a Chevrolet Niva (VAZ-2123). Tightening torque for the cylinder head of a VAZ-2112 16 valves (PRIORA) The tightening torque for the cylinder head on a Priora is taken from the vehicle’s operating manual and is indicated in plate No. 2.
Install the head on the block, first making sure that the crankshaft and camshafts are in the TDC position (both valves of the 1st cylinder must be closed). Tighten the cylinder head mounting bolts in the sequence shown in Fig. 5.6, in four stages: 1st – torque 20 N m (2 kgf m); 2nd – torque 69.4–85.7 N m (7.1–8.7 kgf m); 3rd – tighten the bolts 90°; 4th – finally tighten the bolts 90°.
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, Nm (kgf*m) |
| Cylinder head bolts | M12x1.25 | 1st - torque 20 Nm (2 kgf*m); 2nd - torque 69.4-85.7 Nm (7.1-8.7 kgf*m); 3rd - tighten the bolts 90°; 4th - finally tighten the bolts 90°. |
| Cylinder head cover bolt | M6 | 1.96-4,60 (0,20-0.47) |
| Cylinder head bolt | M8 | 31,36-39,10(3,20-3,99) |
Table No. 2.
Priora cylinder head tightening torque. It is necessary to take into account that:
The cylinder head bolts become stretched with repeated use. Replace bolts whose length (excluding head height) exceeds 98 mm with new ones. Before installing the cylinder head, lubricate the bolts with a thin layer of engine oil.
Tightening torque of the cylinder head KALINA, GRANT
The tightening torque of the cylinder head on engines model 21114-50 installed on Lada Kalina cars are indicated in table No. 3. The 21114-50 engine is based on the VAZ-2111 engine. Increasing the engine displacement of model 21114 to 1.6 liters. compared to engine capacity 2111, achieved due to a larger piston stroke with a constant cylinder diameter.
The combustion chamber in the head of the engine block of the model 21114 has become larger compared to the 2111 engine: its length has increased from 79 to 81 mm, and its width from 48 to 50 mm. To distinguish the block heads, there is a boss with the number “11183” next to the threaded hole for the spark plug of the 1st cylinder of the engine head, model 21114.
Here's what the instruction manual tells us about the tightening torque of the cylinder head on a viburnum:
Install the head on the block, first making sure that the crankshaft and camshaft are in the TDC position (both valves of the 1st cylinder must be closed). Tighten the cylinder head mounting bolts in the specified sequence in four stages: 1st - to a torque of 20 Nm (2 kgf*m); 2nd - torque 69.4-85.7 Nm (7.1-8.7 kgf*m) 3rd - tighten the bolts 90°; 4th - finally tighten the bolts 90°.
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, Nm (kgf*m) |
| Cylinder head bolts | M12x1.25 | 1st - torque 20 Nm (2 kgf*m); 2nd - torque 69.4-85.7 Nm (7.1-8.7 kgf*m); 3rd - tighten the bolts 90°; 4th - finally tighten the bolts 90°. |
| Cylinder head cover nut | M6x1.25 | 1,96-4,6 (0,2-0,47) |
Table No. 3.
Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) KALINA engine model 21114, GRANT. Tightening torque of the cylinder head of VAZ 2106, 2107, 2103 The tightening torque of the cylinder head on engines 2106 and 21011, 2103 is the same and is shown in table No. 4. Depending on the model or modification of the car, three types of engines were installed:
- 2106 - with a displacement of 1.6 liters. This is the main engine for the VAZ-2106 car.
- 2101 - with a displacement of 1.3 liters. Installed on VAZ-21063 cars. It differs from the 2106 engine with a piston stroke reduced by 14 mm, therefore it has a different cylinder block, crankshaft and other parts of the chain drive of the gas distribution mechanism.
- 2103 - with a displacement of 1.45 liters.
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, Nm (kgf*m) |
| Cylinder head bolts | M12x1.25 | Pre-tightening: min: 33.3 N-m (3.4 kgf*m) - max: 41.16 N-m (4.2 kgf*m); Final tightening min: 96 N-m (9.8 kgf * m) - max: 118.4 N-m (12.1 kgf * m); |
| Cylinder head bolts | M8 | minimum: 30.67 N-m (3.13 kgf*m) - maximum: 39.1 (3.99 kgf*m) |
Table No. 4.
Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) of VAZ-2106. Tightening torque of the cylinder head of VAZ 2108, 2109 The tightening torque of the cylinder head on the VAZ-2108, VAZ-2111-80 engines are the same and are shown in table No. 5.
Tighten the head mounting bolts in the specified sequence in four stages: 1 - to a torque of 20 Nm (2 kgfm); 2 - torque 69.4-85.7 Nm (7.1-8.7 kgf-m); 3 - tighten the bolts 90°; 4 - finally tighten the bolts 90°.
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, Nm (kgf*m) |
| Cylinder head bolts | M12x1.25 | 1 - torque 20 N-m (2 kgf-m); 2 - torque 69.4-85.7 Nm (7.1-8.7 kgf-m); 3 - tighten the bolts 90°; 4 - finally tighten the bolts 90°. |
Table No. 5. Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) of VAZ-2108, 2109.
The cylinder head bolts become stretched with repeated use. Replace with new bolts whose length exceeds 135.5 mm. Before installing the cylinder head, lubricate the bolts with a thin layer of engine oil.
Tightening torque for cylinder head VAZ 2108, 2110, 2114 8 valve injector, 2115
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, Nm (kgf*m) |
| Cylinder head bolts | M12x1.25 | 1 - torque 20 N-m (2 kgf-m); 2 - torque 69.4-85.7 Nm (7.1-8.7 kgf-m); 3 - tighten the bolts 90°; 4 - finally tighten the bolts 90°. |
Table No. 6.
Tightening torque of the cylinder head of VAZ 2108, 2110, 2114, 2115. Tightening torque of the cylinder head of VAZ 2101. The tightening torque of the cylinder head given in table No. 7 is used for engines of the following models:
- VAZ-2101 with a displacement of 1.2 liters. This is the main engine for VAZ-2101 cars;
- VAZ-21011 with a displacement of 1.3 liters. Installed on VAZ 21011 and VAZ-21021 cars. It differs from the previous model by increasing the cylinder diameter by 3 mm, so it has a different cylinder block and piston; The cylinder head tightening torque is similar to that of the VAZ 2101;
- VAZ-2103 with a displacement of 1.45 liters. It differs from the first model with a piston stroke increased by 14 mm, so it has a different cylinder block and connecting rod-piston group. The tightening torque of the cylinder head bolts is similar to the VAZ-2101 engine.
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, Nm (kgf*m) |
| Cylinder head bolts | M8 | 31.36-39.1 |
| Cylinder head cover bolt | M6 | 1.96-4.60 |
Table No. 7. Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) VAZ 2101. Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) OKA-1111, 11113
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, Nm (kgf*m) |
| Cylinder head nuts | — | 77-82 |
Table No. 8.
Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) OKA-1111, 11113. Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) NIVA Tightening torques for VAZ-21214 Euro3 engines.
Fig.3 Tightening procedure for NIVA cylinder head
To ensure a reliable seal and avoid tightening the cylinder head bolts during vehicle maintenance, tighten them in four steps. The tightening order is shown in the figure.
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, Nm (kgf*m) |
| Cylinder head nuts | — | Step 1: tighten bolts 1-10 with a torque of 20 (2.0); 2nd reception: bolts 1-10 with a torque of 69.4-85.7 (7.1-8.7). Bolt 11 - torque - 31.4-39.1 (3.2-4.0) |
Table No. 9. Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) NIVA, engines.
Required spare parts
At the same time as updating the 7A-FE timing belt, it is recommended to pay attention to the need to replace other parts:
- belt tensioner;
- spark plug well seals and valve cover washers;
- camshaft and crankshaft seals;
- spark plug;
- valve cover gasket;
- breather valve bushing;
- alternator, air conditioning and power steering belts.
We dismantle the old spark plug well seals
Cylinder head tightening torque on ZMZ engines.
ZMZ engines are represented by modifications ZMZ-402.5, ZMZ-402.6, ZMZ-4061, ZMZ-4063, ZMZ-40522, ZMZ-40524. The cylinder head tightening torques for these engine models have different values.
Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) on 402 engines (GAZELLE), modifications of ZMZ-4025,4026 engines.
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, Nm (kgf*m) |
| Cylinder head nut | — | 85-90 (8,5-9) |
| Rear cylinder head cover bolt | — | 11-16 (1,1-1,6) |
| Cylinder head cover bolt | — | 4,5-8 (0,45-0,8) |
Table No. 10. Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) of ZMZ 4025 and ZMZ-4026. Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) on 406 engines, modifications ZMZ-4061, ZMZ-4063, ZMZ-40522.
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, Nm (kgf*m) |
| Cylinder head bolt | — | 1) Pre-tightening: 69-82(6.9-8.2); 2) Hold for at least 1 minute 15 seconds - and final tightening - Turn to an angle of 70-75 degrees. |
Table No. 11. Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) ZMZ-4061, ZMZ-4063, ZMZ-40522. Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) on 405 and 405 Euro3 engines, modification ZMZ-40524.
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, Nm (kgf*m) |
| Cylinder head bolt | — | 1) Pre-tightening: 40-50(4.0-5.0); 2) Hold for at least 1 minute 15 seconds - and final tightening - Turn to an angle of 90 degrees. |
Table No. 12. Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) ZMZ-40524. Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) on ZMZ-409 engines.
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, Nm (kgf*m) |
| Cylinder head bolt | — | 1) Pre-tightening: 40-60(4.0-6.0); 2) final tightening: 130-145 (13.0-14.5) |
Table No. 13. Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) ZMZ-409.
The sequence of tightening the cylinder head bolts is shown in the figure.
Tightening torque for GAZ-53 cylinder head.
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, Nm (kgf*m) |
| Cylinder head nuts | — | 77-82 |
Table No. 14.
Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) of GAZ-53. Tightening torque of the KAMAZ-740 cylinder head The tightening torque on the KAMAZ-740.10, KAMAZ-7403.10 or KAMAZ-740.11-240 engines is the same and is shown in table No. 15.
| Detail | Thread | Tightening torque, Nm (kgf*m) |
| Cylinder head bolts | M16 | 157 — 176 (16 — 18) |
Table No. 15.
Tightening torque of the cylinder head (cylinder head) of KAMAZ-740. There are no similar entries.
Dismantling of attachments
Replacing the timing belt on the 7A-FE engine begins with the work of dismantling the attachments. First of all, we put the car on a jack on the right front wheel side. A support is installed under the spar; we remove the jack, since it will be useful in the future.
We dismantle the right side of the engine protection, and also remove the high-voltage wires, spark plugs and two hoses.
The next step is to dismantle the 7A-FE valve cover; to do this, you need to unscrew the four nuts at the corners of the structure. Next, we bend the restrictive antennae and, using a hammer and screwdriver, knock out the old seals.
Then you need to loosen the nuts of the power steering, compressor and generator. To directly remove the belt, you must first loosen two bolts: an adjusting bolt and a locking bolt.
Next, we make sure that the pulley mark coincides with mark 0. The wheel must be securely fixed, and then the fastening nut must be removed. After this, you need to remove the pulley itself and the tension roller.
You also need to install a jack under the 7A-FE engine and remove the power plant support, for which you need to unscrew six nuts.
Replacing oil seals
The next step is to remove the camshaft pulley and loosen the four pump roller nuts. We screw in two self-tapping screws and use pliers to remove the old oil seal. The rigidity of the old oil seal indicates the need to install a new part in its place. Collection is carried out in reverse order.
Power unit marking 4Y
The 2.2 liter engine from the Japanese manufacturer Toyota 4Y is the final one in the Y engine line. Its mass production began back in 1985. And as you know, a new formula for marking Japanese engines was introduced two years later, in 1987. Consequently, all engines comply with the old powertrain naming rules. These rules differ significantly from modern ones.
So, according to the modern formula, there is a symbol in front of it in the form of a number; it means the generation of engines of this family. Everything was different before. The first engine in the 1Y motor line was considered to be the basic one. And all other engines in this line are modifications of the base internal combustion engine. For example, the 3Y engine, the third engine in the Y line, was considered the second modification of the basic 1Y engine. According to modern rules, this would be an engine from the third generation Y engine line.
According to the above, according to the old formulation, the 4Y power unit considered here is considered the third modification of the main engine of this 1Y line. And this despite the fact that 4Y itself has its own two modifications. Previously, they were called versions of the third modification of the main engine. Currently, the concepts version and modification mean approximately the same thing.
Technical data
The fourth engine in the Y line is a four-stroke power unit fueled by gasoline. The engine is four-cylinder, has an in-line arrangement of cylinders. The manufacturer of 4Y is Toyota. This engine was produced from 1985 to 1997. However, its design attracted the interest of Chinese engine builders. Therefore, the engine is successfully produced in our time under the Chinese brands Q491 ME, GW491 QE.
The cylinder block is made of particularly durable cast iron alloy. The BC head is made of aluminum. The intake manifold is made of duralumin; the exhaust manifold, due to the possibility of temperature deformation, is made of cast iron alloy.
The gas distribution mechanism is OHV type, with a lower camshaft and upper valves.
Models of cars in which the Toyota 4Y engine was installed
The 4Y engine was installed on cars produced by the engine developer himself:
The subsidiary also found room for 4Y:
The attractiveness of the technical parameters was the reason for the installation of 4Y in the brainchild of other automakers:
To this day, the engine is successfully installed on loaders. This includes both Toyota’s personal special equipment, for example, Toyota 6FG10, and vehicles from other manufacturers. For example, Geneo 8FG is produced primarily only with a 4Y motor.
Toyota 4Y engine installed on a Daihatsu Rocky car
Possible engine tuning options
Engine tuning is quite a rare occurrence. The reason for this is:
Since the engine has great potential, its tuning is possible in two stages:
Increasing the working volume of the cylinder-piston group
An increase in power leads to a decrease in resource. Descriptions of the consequences of tuning in the form of jammed pistons are a common occurrence. Before embarking on modernization, it is important to plan what course of action is foreseen.
Operational Maintenance 4Y
The most frequent and important maintenance activity for the motor in question is replacing the motor lubricant. Details of the procedure are described in detail in the chapter “Description of the power unit”.
Seal leakage
After a decent mileage, oil seals and gaskets may leak. The problem can be solved by converting the engine to SAE 15W40, 10W40, 5W40.
Timing mechanism
Serious problems may appear on the motor in question due to a malfunction of the timing drive mechanism. The fact is that when the timing chain breaks, the engine deforms the valves. The manufacturer guarantees flawless operation of the drive for 100 thousand km. However, there are known cases of circuit breakage at an earlier period. Therefore, after 30 thousand km, the timing drive mechanism must be thoroughly inspected. And after 60 thousand km, mileage, replace the timing chain and other mechanism parts.
Filters
The filter element for air purification needs to be updated every 10 thousand km. Also, after this period, it is necessary to clean the contaminants in the radiator grilles that interfere with heat transfer and cooling of the engine, and the level of antifreeze should also be monitored. After 60 thousand km, the coolant must be completely replaced.