The Toyota brand is considered one of the best brands in the Japanese automobile industry. Cars from this manufacturer are very popular all over the world.
But, like any equipment, these machines can give out “surprises” to their owner. What to do if the check light comes on in your car? How to find out the true cause of a breakdown and quickly eliminate it?
When receiving information about an error in the operation of a Toyota RAV4, the car owner must worry about eliminating it.
What does error B1811 mean?
Any signal about a problem inside the car is immediately alarming. To find out the exact location of the fault, you need to diagnose the complex mechanism of the Toyota RAV IV.
An OBD2 scanner is used for this. When connecting the device to the diagnostic connector of the car, the driver will receive an error code. Having deciphered it, we obtain complete information about the source of the malfunction. Sometimes this is general information, but the problem can be much more serious.
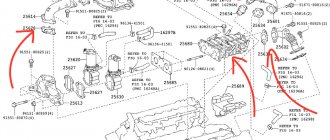
Error B1811 indicates a malfunction of the airbag, namely an open circuit in the driver's front seat.
Main reasons:
- the squib of the second stage of the airbag has failed;
- the SRS control unit indicates a fault in the twisted cable;
- breakdown of the SRS unit itself.
Where is the fault located:
- instrument panel wiring;
- twisted cable;
- SRS control unit.
How to check your security system
After detecting primary symptoms, check:
- select the Signal Check test mode on the GTS to create the illusion of a malfunction;
- start driving on roads with uneven surfaces or move the airbag wiring and connectors
- disconnect the wiring of the central control unit of the SRS system
- check for a short circuit by measuring the voltage with the ignition on. To do this, disconnect the negative battery and connect the CBU wire to it.
As a result, they receive confirmation of the presence of signs of malfunction or their absence.
Advice. After removing the equipment wire from the negative terminal of the battery, you must wait up to 2 minutes to avoid triggering the SRS system.
The main thing is to correctly diagnose error B1811 Toyota RAV4 and determine the source of the problem. Incorrect diagnosis can lead to the purchase of expensive components and additional unnecessary vehicle repairs.
And remember, in order to find out which unit has failed, you need to understand the principle of operation of the equipment.
You can discuss this topic in the comments or on our forum for RAV4 owners.
Causes of malfunction
This type of breakdown refers to problems with electrical and electronics, so you need to contact a technician and diagnose the car wiring.
The main causes of error B1181 in Land Cruiser:
- unsuccessful steering wheel change (loop cable break);
- breakage of the driver's seat position sensor;
- rupture of electrical connections in wires;
- foreign objects falling under the seat (bottles, bags, boxes);
- breakage of the sensor under the driver's seat (the passenger caught it with his foot, etc.);
- moisture getting under the front seat;
- break in the circuit on the steering wheel loop;
- broken wires in the steering column area.
Most vehicle owners solve this problem by completely changing the snail design. To save money, you can resolder the wires or get by with changing the internal cable.
Sometimes the problem lies not in the steering wheel, but in the driver's seat. The control panel is activated when there is a break in the signals in the sensor under the seat. In this case, it is enough to re-solder the sensor connector.
How to troubleshoot and clear the error
Restoring the cable or changing the block helps to quickly fix the problem.
If the driver does not have specialized knowledge, a professional electrician should change the steering cable and the sensor under the seat.
You can do the following on your own:
- try resetting scanner errors;
- check the area under the seat for moisture;
- remove rolled objects under the chair;
- re-solder the terminals of the spiral contacts of the steering wheel.
After repairs have been made and the fault has been eliminated, an error may continue to be displayed on the scanner panel.
To remove a blinking reminder, you need to reset it by following a few simple steps. Before you begin, you need to prepare the connector for diagnostics.
Resetting codes is done as follows:
- Turn on the ignition.
- At the DLC1 connector, short-circuit the TC and E1 terminals with a wire.
- Press the brake pedal more than 10 times at short intervals.
- Make sure that the light constantly lights up at intervals of half a second.
- Turn off the ignition.
- Remove the jumper from the contacts.
- Make sure the ABS scanner indicator goes off.
An electrical problem is a common problem in Toyota vehicles that needs to be fixed. However, do not panic when the scanner signals persistently: after the cause of the breakdown is found, error B1181 is eliminated quite quickly. Repairs will cost about 40-50 dollars.
Technical problems appear over time in any car, including Japanese brands. Defects in Toyota are indicated by codes, which each driver is recommended to decipher independently. Error 1181 is one of the most common types of malfunction. Car owners often have difficulty finding the causes of this problem.
TEST SEQUENCE
- Perform a test that simulates the fault condition by selecting Active Diagnostic Mode (Signal Test Mode) on the handheld scan tool (Click here).
- With Active Diagnostic Mode (Signal Test Mode) selected, perform a test that simulates fault conditions by wiggling each SRS connector or driving on suburban or rough roads (Click here).
Disconnect the cable from the negative (-) battery terminal and wait at least 90 seconds.
Check the correct connection of the connectors of the left front seat belt with the reel and pretensioner assembly.
OK: The connector is connected correctly.
HINT: If the connector is not securely connected, reconnect it and proceed to the next test.
Disconnect the connector from the left front belt with reel and pretensioner assembly.
Check that the No. 2 floor wire connector (left front seat belt side with reel and pretensioner assembly) is not damaged.
OK: The lock button is not released and the lock latch is not deformed or damaged.
Connect SST (2.1 ohm resistance) to connector C.
WARNING: Never connect the handheld tester to the left front belt reel/pretensioner assembly (left front pretensioner squib) for measurement as this may result in serious injury due to air bag deployment.
- When connecting, do not force the SST into the connector pins.
- Insert SST straight into the connector pins.
Connect the cable to the negative (-) terminal of the battery and wait at least 2 seconds.
Turn the ignition ON (IG) and wait at least 60 seconds.
Clear stored DTCs (Click here).
Turn the ignition ON (IG) and wait at least 60 seconds.
OK: DTC B1905, B1906, B1907, B1908 or 74 is not output.
HINT: Codes other than DTCs B1905, B1906, B1907, B1908 and 74 may be output at this time and are not associated with this test.
Result:
| Result | Next step |
| NG | A |
| OK (except 3-door hatchback model) | B |
| OK (for 3-door hatchback model) | C |
Disconnect the cable from the negative (-) battery terminal and wait at least 90 seconds.
Disconnect SST from connector C.
Check that the connectors are correctly connected to the SRS central control unit assembly.
OK: The connector is connected correctly.
HINT: If the connector is not securely connected, reconnect it and proceed to the next test.
Disconnect the connectors from the SRS central control unit.
Make sure the connector pins are not damaged.
OK: The contacts are not deformed or damaged.
Check that the short spring of the anti-trigger floor cable connector is not deformed or damaged.
OK: The short spring is not deformed or damaged.
Connect the cable to the negative (-) terminal of the battery and wait at least 2 seconds.
Turn on the ignition (IG).
Measure the voltage according to the values given in the table.
Rated voltage:
| Contacts for connecting a diagnostic tool | Switch position | Specified conditions |
| L4-1 (L+) - mass | Ignition on (IG) | Less than 1 V |
| L4-2 (L-) - mass | Ignition on (IG) | Less than 1 V |
Disconnect the cable from the negative (-) battery terminal and wait at least 90 seconds.
Measure the resistance according to the values given in the table below.
Nominal resistance:
| Contacts for connecting a diagnostic tool | Switch position | Specified conditions |
| L4-1 (L+) - L4-2 (L-) | Always | Less than 1 ohm |
Measure the resistance according to the values given in the table below.
Nominal resistance:
| Contacts for connecting a diagnostic tool | Switch position | Specified conditions |
| L4-1 (L+) - mass | Always | 1 MΩ or more |
| L4-2 (L-) - mass | Always | 1 MΩ or more |
Open the anti-trigger mechanism built into connector B (Click here).
Measure the resistance according to the values given in the table below.
Nominal resistance:
| Contacts for connecting a diagnostic tool | Switch position | Specified conditions |
| L4-1 (L+) - L4-2 (L-) | Always | 1 MΩ or more |
Return the anti-trigger mechanism of connector B to its original state.
Connect the connectors to the left front belt reel and pretensioner assembly and the SRS central control unit.
Connect the cable to the negative (-) terminal of the battery and wait at least 2 seconds.
Turn the ignition ON (IG) and wait at least 60 seconds.
Clear stored DTCs (Click here).
Turn the ignition ON (IG) and wait at least 60 seconds.
OK: DTC B1905, B1906, B1907, B1908 or 74 is not output.
HINT: Codes other than DTCs B1905, B1906, B1907, B1908 and 74 may be output at this time and are not associated with this test.
Causes of malfunction
This type of breakdown refers to problems with electrical and electronics, so you need to contact a technician and diagnose the car wiring.
The main causes of error B1181 in Land Cruiser:
- unsuccessful steering wheel change (loop cable break);
- breakage of the driver's seat position sensor;
- rupture of electrical connections in wires;
- foreign objects falling under the seat (bottles, bags, boxes);
- breakage of the sensor under the driver's seat (the passenger caught it with his foot, etc.);
- moisture getting under the front seat;
- break in the circuit on the steering wheel loop;
- broken wires in the steering column area.
Most vehicle owners solve this problem by completely changing the snail design. To save money, you can resolder the wires or get by with changing the internal cable.
Sometimes the problem lies not in the steering wheel, but in the driver's seat. The control panel is activated when there is a break in the signals in the sensor under the seat. In this case, it is enough to re-solder the sensor connector.
How to troubleshoot and clear the error
Restoring the cable or changing the block helps to quickly fix the problem.
If the driver does not have specialized knowledge, a professional electrician should change the steering cable and the sensor under the seat.
You can do the following on your own:
- try resetting scanner errors;
- check the area under the seat for moisture;
- remove rolled objects under the chair;
- re-solder the terminals of the spiral contacts of the steering wheel.
After repairs have been made and the fault has been eliminated, an error may continue to be displayed on the scanner panel.
To remove a blinking reminder, you need to reset it by following a few simple steps. Before you begin, you need to prepare the connector for diagnostics.
Resetting codes is done as follows:
- Turn on the ignition.
- At the DLC1 connector, short-circuit the TC and E1 terminals with a wire.
- Press the brake pedal more than 10 times at short intervals.
- Make sure that the light constantly lights up at intervals of half a second.
- Turn off the ignition.
- Remove the jumper from the contacts.
- Make sure the ABS scanner indicator goes off.
An electrical problem is a common problem in Toyota vehicles that needs to be fixed. However, do not panic when the scanner signals persistently: after the cause of the breakdown is found, error B1181 is eliminated quite quickly. Repairs will cost about 40-50 dollars.
All errors TOYOTA 4RUNNER, ALLEX, ALLION, ALPHARD, ALTEZZA, ARISTO, AURION, AURIS, AVALON, AVENSIS, AYGO, BB, BELTA, BLADE, BREVIS, CALDINA, CAMI, CAMRY, CELICA, CELSIOR, CENTURY, COROLLA, ECHO, ESTIMA , FJ CRUISER, FORTUNER, FUNCARGO, GT86, HARRIER, HIACE, HIGHLANDER, HILUX, INNOVA, IPSUM, iQ, ISIS, IST, KLUGER HYBRID, KLUGER V, LAND CRUISER, LAND CRUISER PRADO, MARK, MARK X, MATRIX, MR 2 , NADIA, NOAH, OPA, PASSO, PLATZ, PREMIO, PREVIA, PRIUS, PROBOX, PROGRES, RACTIS, RAUM, RAV4, RUSH, SAI, SEQUOIA, SIENNA, SIENTA, SOLARA, TACOMA, TUNDRA, URBAN CRUISER, VANGUARD, VELLFIRE, VENZA, VERSO, VITZ, VOLTZ, VOXY, WILL CYPHA, WILL VS, WINDOM, WISH, YARIS.
From english:
Decoding the error B1906/74 from Toyota: Open or Short Circuit in ABS Motor Relay Circuit
Make:
Toyota
Code:
B1906 74
Definition:
Open or Short Circuit in ABS Motor Relay Circuit
Description:
The motor relay contact is OFF for 0.2 sec.or more immediately after the motor relay is turned ON.
Cause:
- ABS motor relay
- ABS motor relay circuit
- Brake actuator assembly
Failure Type:
Actuator Slipping
This sub type is used for failures where the control module detects excessive duration to command a motor, solenoid, relay, etc., to move a piece of equipment to a desired position.
Selecting a scanner
There are many scanners for sale that differ in functionality and price. An inexperienced driver may have dazzle in the eyes from such a choice. Therefore, let’s simplify the task and focus on three popular devices for diagnosing the Prado 120.
Car scanner Delphi DS150E
Delphi DS150E
Country: USA. Place of production: China.
Price 6 thousand rubles.
Pros:
Good price-function ratio. The scanner software contains a database of hundreds of cars, both trucks and cars of all popular models. The connection plug here is standard OBD-ƖƖ. A good device for personal use.
ODB-II connector for Delphi DS150E scanner
Minuses:
Here we can say that the functionality is slightly limited, but this disadvantage is not compensated by the low price.
Autoscanner Launch CReader V+
Launch CReader V+
Country China
Price about 3500 rubles
Pros:
LCD display of the Launch CReader V+ scanner
Price. The device is equipped with a liquid crystal display, which makes it autonomous. Diagnostics do not require connection to a laptop or smartphone. Diagnostic data can be displayed in two formats to choose from - text or graph. Reads Prado 120 error codes at a good level.
Diagnostic data can be displayed in two formats - text or graph.
Minuses:
May not detect some protocols. Powered by a built-in battery, which discharges quickly in the cold.
Car scanner Delphi TCS CDP+USB+BlueTooth
Delphi TCS CDP+USB+BlueTooth
Country USA, made China
Price 11 thousand rubles.
Pros:
Diagnostic interface: Autocom
The scanner is capable of working with different diagnostic interfaces: Autocom, Wow or Delphi in Windows 10. The software contains information about 4000 car models. In addition to reading errors, the device can calibrate sensors, program injectors and key fobs. There is also an on-board recorder function without using a computer, which allows you to identify many faults in electronic systems.
Diagnostic Interface: Wow
It is possible to reset the service interval and control all vehicle systems. At a relatively low price, the functionality is close to professional.
Diagnostic interface: Delphi
Minuses:
If the scanner is needed only to simply identify Prado 120 errors, then this is not the optimal choice.
We carry out computer diagnostics
Diagnostics of the Land Cruiser Prado 120 using a Lexus dealer scanner To test the components and assemblies of the Toyota Land Cruiser Prado 120 for possible errors, scanning devices are used.
Accurate results are provided by specialized dealer scanners. In addition to them, there are universal devices. The simpler the scanner, the more likely it is that it will not recognize Prado 120 specific errors. However, most faults will be deciphered. Faults are read using the same algorithm:
- Stop the engine and turn off the ignition.
- Connect the scanner to the Prado 120 diagnostic connector.
- If the scanner is not connected to a computer, connect it to a laptop or phone.
- If the connection is via Bluetooth, use a smartphone.
- The diagnostic program must be loaded into the computer. After launching it, mark the make and model, year of manufacture of the machine, as well as the type of scan.
- Turn on the ignition, wait until the car’s on-board computer performs self-diagnosis.
- Start the scanning process.
- After checking the control units, the program will display the errors accumulated in them.
- Rewrite the issued Prado 120 error codes. Some programs decipher them independently. If there is no such function, then information can be found on the Internet.
- Clear the errors, drive the Prado 120 for 5 - 10 kilometers. Run diagnostics again. After this, the program will show only current problems. The disappeared may carry information about a sensor that once turned off and then started working again, and the like. Such errors may appear again during subsequent operation of the vehicle. But for now we are only interested in active faults.
- We record errors.
- If the Prado 120 is diagnosed professionally at a car service center, then the next step is dynamic scanning. This check allows you to obtain information about the ignition timing, temperature conditions, instantaneous fuel consumption and other data on engine operation. Dynamic diagnostics are performed with the engine running.
- Other car units are scanned in the same way: brakes, air conditioning, air suspension, immobilizer, gearbox, etc.
- After completing the diagnostics, turn off the ignition, then disconnect the scanning device from the connector in the car.
Now you can analyze the errors and take measures to eliminate them.
Common mistakes on Toyota Rav 4
| Error code | Decoding |
| c1298 | Detection of this fault code means that the pressure control solenoid device is not functioning properly. It is necessary to check whether the mechanism is intact. If yes, then you need to check the wiring and then the all-wheel drive control module |
| S1201 | This error code is recorded when the engine speed is below the set limit. It is necessary to check the idle speed sensor and diagnose the shafts. It is necessary to check the power unit. |
| P1047 | Code P1047 may appear when a problem is detected in the Valvematic module settings. It is possible that power supply circuit B1 is damaged. |
| P2646 | The detected fault code makes it clear that the VTEC sensor does not receive information about the presence of pressure, and the valve opens |
| P1750 | Code P1750 appears when there is a problem with the brake system control unit. |
| P0138 | Combination P0138 is a sign that the oxygen output level in the first tank has been exceeded. |
| P2757 | When P2757 is detected, you should check the operation of the DSU sensor on the transmission. |
| P1604 | Code P1604 may appear on cars produced in 1992, 1997, 1993, when there was an unsuccessful attempt to start the engine. This can happen for several reasons: |
Errors Prado 120
Let's look at the common Prado 120 error codes that diagnostics detect.
B1153
Error B1153 (Airbag Error)
Error B1153 Prado 120 means: malfunction of the seat position sensor. This often means that the driver's seat sensor wire is damaged. To fix the problem, you need to remove the seat; on the bottom right side of it is the part we need. We find and eliminate the break.
We remove the seat; on the bottom right side of it is the part we need. We eliminate the break.
P0051
Error P0051: Oxygen Sensor Malfunction
P0051 error Prado 120 means a malfunction of the oxygen sensor. It is treated by replacing the damaged device. It can be removed using a wrench. The removed “oxygen tube” must be ringed. If it is working properly, then the problem is a clogged catalyst, the passage of gases through which deteriorates and affects the sensor readings.
Oxygen sensor Land Cruiser Prado 120
S1223 and S1246
Errors C1223 and C1246 Land Cruiser Prado 120
Errors C1223 and C1246 Prado 120 are related to ABS. C 1223 reports a general system malfunction, and c1246 indicates that the problem is with the pressure sensor in the master cylinder.
When driving, this is manifested by the ABS fault indicator constantly glowing on the dashboard and the cruise control not working.
ABS Land Cruiser Prado 120 is on
When scanning the system, we display the signals of the brake light sensor and pressure sensor on the display in graphical form. When you press the brake pedal, the graph shows an increase in pressure in the circuit, but the stop signals are not activated. The ABS unit does not receive a signal from the brake pedal.
We check the fuse box - the fault is most likely there. We replace the burnt element.
Fuse box Land Cruiser Prado 120
But if the cause of the fuse blown is not eliminated, the problem will reappear. Operating experience of the Prado 120 suggests that the reason is a damaged towbar socket.
Damaged towbar socket
What does error B1181 mean on Prado
Error B1181 that appears on the display is a malfunction of Toyota Prado 120 vehicles. Indicates a break in the circuit of the second stage of the driver’s airbag. A red icon or image of a pregnant woman lights up on the panel. The scanner displays an error number.
This code in most cases indicates that there is a problem with the spiral cable inside the steering wheel.
Error b1181 Land Cruiser 100 - occurs as often as on the Toyota Prado model.
To correct the defect, you need to diagnose the Toyota's operation. Before starting an electronics check, the driver must make sure that all mechanisms are in satisfactory condition. It is necessary to check the electrical wiring, all fuses, inspect the fasteners and components.
Causes of malfunction
This type of breakdown refers to problems with electrical and electronics, so you need to contact a technician and diagnose the car wiring.
The main causes of error B1181 in Land Cruiser:
- unsuccessful steering wheel change (loop cable break);
- breakage of the driver's seat position sensor;
- rupture of electrical connections in wires;
- foreign objects falling under the seat (bottles, bags, boxes);
- breakage of the sensor under the driver's seat (the passenger caught it with his foot, etc.);
- moisture getting under the front seat;
- break in the circuit on the steering wheel loop;
- broken wires in the steering column area.
Most vehicle owners solve this problem by completely changing the snail design. To save money, you can resolder the wires or get by with changing the internal cable.
Sometimes the problem lies not in the steering wheel, but in the driver's seat. The control panel is activated when there is a break in the signals in the sensor under the seat. In this case, it is enough to re-solder the sensor connector.
Reset errors
If you repair the faulty unit that the computer pointed to, then sometimes it is not possible to completely remove the error on the Prado 120. These include:
- Check Engine;
- ABS OFF;
- VSC, TRC.
If the Prado car has recently been repaired, the blinking of these lights brings moral concern to the car enthusiast. He is worried about the health of his vehicle.
In order not to see errors on the screen, you can reflash the electronic control unit of the machine or reset it using a scanner. To disable them using computer equipment, you need to go to a service center, or do everything yourself.
If the car owner has a scanner at home and knows how to use it, then you can reset the Check Engine and other fault codes as follows:
- Connect the device to the car's diagnostic connector, which is located under the steering wheel.
- Install the holder from the scanner into a laptop with software for searching for fault codes of car components.
- Turn on the ignition and the laptop with the scanner.
- Find the section with fault codes and click on the “Erase” button.
All machine fault numbers will be automatically deactivated. But you need to be sure that the breakdown is really corrected, since the Prado 120 TLK ECU, with working parts, independently deletes the breakdown notification.
Errors in the operation of body systems B1901 of a Toyota vehicle (TYO)
Taking into account the fact that OBD2 errors in the operation of a car’s electronic systems do not always directly indicate a non-functioning element, but more often they provide only general information about the malfunction, we came to the following conclusion:
In different brands and models of cars, the same error can occur as a result of the malfunction of completely different elements.
It became clear that a resource was simply needed in which one could find not only general information about the OBD2 error, but also practical data on a specific car.
The experience of auto electricians has shown that if we consider a specific make and model of a car, then in the vast majority of cases the cause of any error is the same.
We are creating, with your help, a directory of cause-and-effect relationships for the occurrence of a particular OBD2 error in a specific car (make and model). If a description (causality) of the error is not found for your car, then do not hesitate to ask a question.
If you have experience in eliminating a particular error, share your experience with other users. This way we can create a useful resource. A drop from each will benefit everyone.
You might be interested:
If the error indicates incorrect parameters (high or low values) of any of the sensors or analyzers, then most likely this element is working, and the problem must be looked for, so to speak, “upstream”, in the elements whose operation is analyzed by the sensor or probe.
If the error indicates a constantly open or closed valve, then you need to approach the issue wisely, and not thoughtlessly change this element. There may be several reasons: the valve is clogged, the valve is jammed, the valve receives an incorrect signal from other faulty components.
Cars are becoming more complex every day, but also more diagnosable. Our forum was created for everyone, from simple car enthusiasts to professional auto electricians.
Table with errors
Full description of error codes for Toyota cars:
General faults
The following components are subject to diagnosis:
- all sensors installed on wheels;
- anti-slip system control unit;
- wires from the ABS control module to the controllers and control unit;
- contacts on the regulators.
Transmission faults
- malfunction of the speed shift sensor;
- gear drive failure;
- damage to the cable or one of the contacts on it;
- software malfunction of the control unit or use of an old version of software (software);
- lack of communication between the engine and gearbox control modules.
Possible causes of the malfunction:
- selection mechanism stroke sensor;
- incorrect operation of the selector drive unit and speed switch assembly (system electric motor);
- automatic transmission module malfunction;
- damage or wear to the shift joint or fork rod.
- malfunction of the drive device for selecting and switching speeds in the assembly;
- short circuit in the transmission electric motor line;
- problems in the operation of the TCM module.
More details on what to check:
- Screen filters for the solenoid valve of the variable valve timing drive. These elements can be clogged or torn, and sometimes they are not installed correctly.
- Leakage of motor fluid at the seating surfaces of the gas distribution valve drive unit seals.
- Interruption of the supply of engine fluid to the solenoid valve of the drive mechanism.
- Integrity of the timing belt for wear.
Possible causes of the problem:
- incorrect compression in the engine cylinders;
- air leak;
- damage to the cylinder head gasket or head;
- faulty or clogged mass air flow sensor;
- failure of the lambda probe or damage to one of the contacts on the devices;
- fuel filter clogged;
- injector malfunction.
- failure or incorrect functioning of the electric pneumatic valve for controlling the turbocharger;
- break or short circuit on the vacuum control line;
- malfunction of the turbocharger device;
- breakdown of the recirculation system valve;
- damage to vacuum pipes or leakage;
- malfunction of the power unit control unit.
- malfunction of the fuel filter device;
- leakage or loosening of the fuel line clamps (you need to check the integrity of the nut for tightening the fuel pump cover and housing);
- breakdown of the fuel pump device.
Possible causes of the malfunction:
- battery discharge or damage;
- malfunction of the ignition switch or Start/Stop system;
- regular use of low-quality fuel;
- problems with the immobilizer;
- malfunction of the anti-theft system;
- critical engine failure;
- clogged one of the filters that affects startup;
- faulty injectors or oxygen sensors.
Sensor malfunctions
To resolve the issue, it is recommended to do the following:
- Check the integrity of the connectors on the block connecting the sensor to the dashboard. Perhaps the contact has come loose and needs to be reconnected.
- Diagnose the integrity of the cable through which the sensor is connected to the instrument cluster.
- Check the quality of the connection between the controller and the transmission unit.
- Carry out diagnostics of contacts for short circuits.
- malfunction of the boost pressure controller, sensor parameters are not within the range of normalized values;
- problems in the functioning of the turbocharger control drive unit.
- damage to the sensor power wiring or the bulbs installed in the brake lights;
- failure of the relay or safety device of the optical elements;
- damage to the fuse socket or contacts;
- malfunction of the sensor installed on the brake pedal;
- problems with the control unit.
- malfunction of the left or right front engine speed controller;
- damage to the wiring supplying the regulator;
- malfunction of the rotor speed mechanism;
- errors made when installing the sensor;
- Malfunction of the brake actuator control module assembly (ABS).
Electrical and electronic faults
Possible causes of the malfunction:
- the heating element has failed;
- the lambda probe fuse is blown;
- the wiring supplying the sensor is damaged, or a short circuit has occurred in the electrical circuit;
- the contact on the controller power supply has oxidized;
- The ECM motor control unit has failed or is not working correctly.
- stopping the engine when idling;
- difficulty starting the engine;
- “triple” of the power unit when driving uphill;
- RPM surges.
Possible causes of the malfunction:
- battery discharge;
- damage to the battery, which led to leakage of electrolyte and its inoperability;
- oxidation of the battery terminals or damage to the clamps;
- generator device malfunction;
- failure of the regulator relay;
- Damage or breakage of the drive belt.
Possible causes of the problem:
- failure of the clutch release actuator device;
- the smoothness of the fork or release bearing is impaired;
- failure of the clutch basket;
- use of non-original spare parts to repair the system;
- errors made when installing parts;
- using a control unit with outdated software.
- line damage or short circuit on the reverse light switch wire;
- failure of the switching mechanism travel controller;
- breakdown of the travel sensor of the selection mechanism;
- a malfunction of the TCM module or a software failure in its operation;
- Reverse light switch is broken.
- the control unit has not calibrated the zero position of the deceleration controller;
- the vehicle position was not stabilized during calibration;
- the SRS control module is faulty or operates intermittently;
- the control unit has failed or is not functioning correctly.
- broken or damaged line of the speed shift solenoid valve SR;
- SLU is shorted or disconnected.
damage to the wires on the instrument cluster or disconnection of contacts;
malfunction of the main wiring harness in the engine compartment;
failure of the left front anti-skid sensor;
Possible causes of the problem:
damage or wear of the harness with electrical circuits connected to the instrument cluster;
malfunction of the twisted wire assembly;
failure or disconnection of the contact from the horn button;
- the anti-skid system control module detects an impulse of a break or damage to the power line of the rear left squib;
- breakdown of the airbag knock sensor;
- failure of the control module or software failure of the SRS device.
- short circuit in the power supply wiring of the driver's knee airbag knock sensor;
- failure of the device's squib;
- breakdown or software malfunction in the operation of the SRS control module.
- Communication error between the engine control module and the ID code block. A detailed diagnosis of the wiring harness is required.
- Communication line failure. It is recommended to diagnose the ECM module.
- Identification element differences detected during the exchange of information between the identifier module and the ECM. It is necessary to check the operation of the modules.
To diagnose, you need to do the following:
- Check the battery. The cause of the problem may be its discharge, which causes the generator to work in increased mode, which leads to an increase in voltage. You need to make sure that there is no damage to the battery case, as well as the integrity of the contact clamps.
- Perform diagnostics on the generator drive belt. If the product is worn out, it must be replaced.
- Check the operation of the generator device. The cause of the problem may be a faulty regulator relay.
To find the cause, perform the following steps:
- the sensor itself is checked - the contact may have come off the device;
- diagnostics of the electrical circuit connected to the sensor is performed;
- The parking radar control unit is diagnosed.
Two-digit Type 9 codes
Possible causes of the malfunction:
- damage to the pins on the connection block;
- cable break or wear of the insulating layer;
- malfunction of the EFI unit itself;
- software problem;
- Battery malfunction.
- candles;
- coils;
- high-voltage wires;
- distributor.
Fault codes are considered for the following Toyota models:
- 4Runner
- Avensis T25 (Avensis T25);
- Avalon (Avalon);
- Auris (Auris);
- Aristo (Aristo);
- Brevis (Brevis);
- Caldina (Kaldina);
- Carina (Karina);
- Cami (Kami);
- Camry V40 (Camry);
- Chaser (Chaser);
- Corolla MMT, Ceres, SV40 (Corolla);
- Corona Premio (Crown Premio);
- Crown 1G FE (Crown);
- Estima (Estima);
- Fielder;
- Isis (Isis);
- Ipsum (Ipsum);
- Gracia (Grace);
- Granvia (Granvia);
- Highlander (Highlander);
- Hilux (Hilux);
- Land Cruiser 200 (Land Cruiser);
- Majesta (Majesta);
- Mark, Mark2 (Mark);
- Nadia (Nadia);
- Noax (Noah);
- Passo (Passo);
- Platz
- Prado (Prado);
- Previa (Previa);
- Prius (Prius);
- Rav4 (Rav 4);
- Soarer (Sorer);
- Surf
- Town;
- Verso (Verso);
- Vista (Vista);
- Vitz (Vitz);
- Wish (Wish);
- Yaris (Yaris);
- Windom (Windom);
Toyota errors via OBDII protocol
Fuel system and air supply
P0000-P0099, P0100-P0199, P0200-P0299
P0010 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the variable valve timing system drive, intake/left/front, bank 1
P0011 - Camshaft Position, Intake/Left/Front, Bank 1 - Valve opening angle too early/system malfunction
P0012 - Camshaft Position, Intake/Left/Front, Bank 1 - Valve opening angle too late
P0015 - Variable valve timing actuator, exhaust/right/rear, bank 1 - opening angle too late
P0016 - Crankshaft and camshaft position, bank 1, sensor A - no match
P0017 - Crankshaft and Camshaft Position Bank 1 Sensor B - Correlation
P0018 - Crankshaft and camshaft position, bank 2, sensor A - correlation
P0030 - Heated Oxygen Sensor 1 Circuit Malfunction, Bank 1 Heater Control
P0031 - Heated Oxygen Sensor 1 Circuit Low Voltage, Bank 1, Heater Control
P0032 - Heated Oxygen Sensor 1 Circuit High Voltage, Bank 1, Heater Control
P0036 - Heated Oxygen Sensor 2 Bank 1 Heater Control Circuit Malfunction
P0037 - Heated Oxygen Sensor 2 Circuit Low Voltage, Bank 1 Heater Control
P0038 - Heated Oxygen Sensor 2 Circuit High Voltage, Bank 1 Heater Control
P0045 - Turbo Boost Control Solenoid/Supercharger Boost Pressure Control Valve - Open Circuit
P0046 - Turbo Boost Pressure/Supercharger Boost Pressure Control Solenoid Valve - Range/Performance
P0047 - Turbo Boost/Supercharger Boost Pressure Control Solenoid Valve - Signal Low
P0048 - Turbocharger/Supercharger Boost Pressure Control Solenoid Valve - Signal High
P004B - Turbocharger/Supercharger Boost Pressure Control B - Range/Performance
P004C - Turbocharger/Supercharger Boost Pressure Control B - Signal Low
P004D - Turbocharger/Supercharger Boost Pressure Control B - Signal High
P0050 - Heated Oxygen Sensor 1 Bank 2 Heater Control Circuit Malfunction
P0051 - Heated Oxygen Sensor 1 Bank 2 Heater Control Low
P0052 - Heated Oxygen Sensor 1 Bank 2 Heater Control High
P0056 - Heated Oxygen Sensor 2 Circuit Malfunction, Bank 2 Heater Control
P0057 - Heated Oxygen Sensor 2 Bank 2 Heater Control Low
P0058 - Heated Oxygen Sensor 2 Bank 2 Heater Control High
P0093 - Significant leak in the fuel system
P00B0 - Turbocharger/supercharger boost pressure control “B” - control unit characteristics
P0100 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the air flow sensor (mass - MAF) / (volume - VAF)
P0101 - Mass Air Flow Sensor (MAF) / (VAF) - Range/Performance
P0102 - Low air flow sensor (MAF) / (VAF) input signal
P0103 - Mass Air Flow Sensor (MAF)/(VAF) Input High
P0104 - Insecure contact in the electrical circuit of the mass air flow sensor (MAF) / (VAF)
P0105 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor / atmospheric pressure sensor
P0110 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the intake air temperature sensor
P0111 - Intake Air Temperature Sensor - Range/Performance
P0112 - Intake air temperature sensor signal low
P0113 - Intake air temperature sensor signal high
P0114 - Intake air temperature sensor - electrical circuit poor contact
P0115 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the coolant temperature sensor
P0116 - Coolant Temperature Sensor - Range/Performance
P0117 - Coolant temperature sensor signal low
P0118 - Coolant temperature sensor signal high
P011B - Coolant Temperature/Intake Air Temperature - Correlation
P0120 - Throttle Position Sensor/Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction
P0121 - Throttle Position Sensor/Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor - Range/Performance
P0122 - Throttle Position Sensor/Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Low
P0123 - Throttle Position Sensor/Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor High
P0124 - Throttle Position Sensor/Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor - Circuit Intermittent
P0125 - Coolant temperature insufficient for closed-loop fuel control
P0130 - O2 Sensor 1 Circuit Malfunction, Bank 1
P0131 - Oxygen Sensor 1 Circuit Low Voltage, Bank 1
P0132 - Oxygen Sensor 1 Circuit High Voltage, Bank 1
P0133 - Oxygen sensor 1 low response, bank 1
P0134 - No response from oxygen sensor 1, bank 1
P0135 - Heated Oxygen Sensor 1 Circuit Malfunction, Bank 1 Heater Control
P0136 - O2 Sensor 2 Circuit Malfunction, Bank 1
P0137 - Oxygen Sensor 2 Circuit Low Voltage, Bank 1
P0138 - Oxygen Sensor 2 Circuit High Voltage, Bank 1
P0139 - Oxygen sensor 2 low response, bank 1
P0140 - No response from oxygen sensor 2, bank 1
P0141 - Heated Oxygen Sensor 2 Bank 1 Heater Control Circuit Malfunction
P0155 - Oxygen Sensor 1 Bank 2 Heater Control Circuit Malfunction
P0156 - O2 Sensor 2 Circuit Malfunction, Bank 2
P0157 - Oxygen Sensor 2 Circuit Low Voltage, Bank 2
P0158 - Oxygen Sensor 2 Circuit High Voltage, Bank 2
P0159 - Oxygen sensor 2 low response, bank 2
P0160 - No response from oxygen sensor 2, bank 2
P0161 - Heated Oxygen Sensor 2 Circuit Malfunction, Bank 2 Heater Control
P0170 - Fuel balance, bank 1 - malfunction
P0171 - Air/fuel mixture too lean, bank 1
P0172 - Air/fuel mixture too rich, bank 1
P0173 - Fuel balance, bank 2 - malfunction
P0174 - Air/fuel mixture too lean, bank 2
P0175 - Air/fuel mixture too rich, bank 2
P0190 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the fuel rail pressure sensor
P0191 - Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor - Range/Performance
P0192 - Low signal level in the electrical circuit of the fuel rail pressure sensor
P0193 - High signal level in the electrical circuit of the fuel rail pressure sensor
P0200 - Malfunction in the injector electrical circuit
P0201 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector No. 1
P0202 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector No. 2
P0203 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector No. 3
P0204 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector No. 4
P0205 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector No. 5
P0206 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector No. 6
P0207 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector No. 7
P0208 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector No. 8
P0209 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector No. 9
P0210 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector No. 10
P0211 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector No. 11
P0212 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of injector No. 12
Ignition system
P0300-P0399
P0300 - Random/multiple misfires (ignition)
P0301 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder No. 1
P0302 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder No. 2
P0303 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder No. 3
P0304 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder number 4
P0305 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder No. 5
P0306 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder number 6
P0307 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder number 7
P0308 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder number 8
P0309 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder number 9
P0310 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder number 10
P0311 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder No. 11
P0312 - Misfire (ignition) in cylinder number 12
P0325 - Knock Sensor 1 Circuit Malfunction, Bank 1
P0326 - Knock Sensor 1 Bank 1 - Range/Performance
P0327 - Knock Sensor 1 Circuit Low, Bank 1
P0328 - Knock Sensor 1 Circuit High, Bank 1
P0329 - Knock Sensor 1, Bank 1 - Circuit Insufficient
P0330 - Knock Sensor 2 Circuit Malfunction, Bank 2
P0331 - Knock Sensor 2 Bank 2 - Range/Performance
P0332 - Knock Sensor 2 Circuit Low, Bank 2
P0333 - Knock Sensor 2 Circuit High, Bank 2
P0334 - Knock Sensor 2, Bank 2 - Circuit Insufficient
P0335 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the crankshaft position sensor
P0336 - Crankshaft Position Sensor - Range/Performance
P0337 - Crankshaft Position Sensor - Low Signal
P0338 - Crankshaft Position Sensor - Signal High
P0339 - Crankshaft Position Sensor - Circuit Inadequate Contact
P0340 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the camshaft position sensor
P0341 - Camshaft Position Sensor - Range/Performance
P0342 - Camshaft Position Sensor - Signal Low
P0343 - Camshaft Position Sensor - High Input
P0344 - Camshaft Position Sensor - Circuit Inadequate Contact
P0345 - Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Circuit Malfunction, Bank 2
P0346 - Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Bank 2 - Range/Performance
P0347 - Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Bank 2 - Signal Low
P0348 - Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Bank 2 - Signal High
P0349 - Camshaft Position Sensor "A" Bank 2 - Circuit Intermittent
P0350 - Ignition Coil Primary/Secondary - Circuit Malfunction
P0351 - Ignition Coil A Primary/Secondary - Circuit Malfunction
P0352 - Ignition Coil B Primary/Secondary - Circuit Malfunction
P0353 - Ignition Coil "C", Primary/Secondary - Circuit Malfunction
P0354 - Ignition Coil "D" Primary/Secondary - Circuit Malfunction
P0355 - Ignition Coil "E", Primary/Secondary - Circuit Malfunction
P0356 - Ignition Coil "F" Primary/Secondary - Circuit Malfunction
P0357 - Ignition Coil "G" Primary/Secondary - Circuit Malfunction
P0358 - Ignition Coil "H" Primary/Secondary - Circuit Malfunction
P0359 - Ignition Coil I Primary/Secondary - Circuit Malfunction
P0360 - Ignition Coil "J" Primary/Secondary - Circuit Malfunction
P0361 - Ignition Coil "K" Primary/Secondary - Circuit Malfunction
P0362 - Ignition Coil "L" Primary/Secondary - Circuit Malfunction
P0368 - Camshaft Position Sensor B, Bank 1 - Signal High
P0393 - Camshaft Position Sensor B, Bank 2 - Input High
Emission control
P0400-P0499
P0400 - Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System - System Channel Malfunction
P0401 - Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system - insufficient recirculation level
P0405 - Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valve position sensor A - signal low
P0418 - Exhaust Air Pump A Relay - Circuit Malfunction
P0420 - Catalytic Converter Bank 1 - Efficiency Less Than Required
P0430 - Catalytic Converter Bank 2 - Efficiency Less Than Required
P0441 - Evaporative Emission System - Incorrect Flow
P0442 - Evaporative Emission System - Minor Leak
P0443 - Evaporative Accumulator Solenoid Valve - Circuit Malfunction
P0446 - Evaporative Emission System, Purge Control - Circuit Malfunction
P0456 - Evaporative Emission System - Extremely Minor Leak
Speed and idle control
P0500-P0599
P0500 - Malfunction in the electrical circuit of the vehicle speed sensor
P0504 - Brake Lamp A/B Switch (Brake Pedal Position Sensor) - Correlation
P0505 - Idle Speed Control System - Malfunction
P0556 - Brake Booster Pressure Sensor - Range/Performance
P0560 - System voltage (on-board network) - malfunction
Electronic control unit (ECU) and its subsystems
P0600-P0699
P0606 - Electronic Engine Control Module (ECM)/Powertrain Control Module (PCM) - Processor Malfunction
Transmission
P0700-P0799, P0800-P0899, P0900-P0999
P0703 - Brake Light Switch "B" - Circuit Malfunction
P0705 - Shift Position Sensor, PRNDL Input - Circuit Malfunction
P0715 - Automatic transmission input shaft speed sensor (torque converter turbine) - electrical circuit malfunction
P0724 - Brake Light Switch "B" - Signal High
P0741 - Torque converter lockup clutch solenoid valve - functioning or stuck closed
P0746 - Transmission fluid pressure control solenoid valve - functioning or stuck closed
P0748 - Transmission fluid pressure control solenoid valve - electrical fault
P0753 - Shift Solenoid Valve "A" - Electrical Malfunction
P0758 - Shift Solenoid Valve B - Electrical Malfunction
P0778 - Pressure control solenoid valve "B" - electrical fault
P0793 - Transmission intermediate shaft speed sensor - no signal
P0810 - Clutch control error
P0812 - Reverse Transmission - Input Circuit Malfunction
P0820 - Shift Lever XY Position Sensor - Circuit Malfunction
P0900 - Clutch actuator - open circuit
P0907 - Transmission Range Select Circuit - High Voltage
P0909 - Transmission Range Selection Error
P0910 - Transmission Range Select Actuator - Open Circuit
P0915 - Gear Detection Circuit - Range/Performance
P0917 - Gear Detection Circuit - Circuit High Voltage
P0919 - Transmission Control - Error
P0974 - Shift Solenoid Valve A - Signal High
P0999 - Shift Solenoid Valve "F" - Signal High
How to diagnose the error?
The self-diagnosis process for Toyota vehicles can only be performed using connectors DLC1 and DLC2.
The test block is made in the form of a small plastic module equipped with a lid. Depending on the car model, the location of the connector may vary, but usually it is located in the engine compartment on the left side. On the block cover there is the inscription “Diagnostic”. In older versions of Toyota, the device is located next to the battery.
For Toyota Karina cars 1992-1997, as well as Corona and Mark 1992, error codes can only be read by reading the blinking LEDs. In newer versions of vehicles, the DLC2 module is located in the vehicle interior. It can be seen under the center console panel or near the driver’s feet, under the steering wheel. The module is made in the form of an oval or circle. The diagnostic process consists of closing certain contact elements of the block, which must be connected in a specific sequence.
Algorithm for checking:
- The protective plastic cover is removed from the connector. On the reverse side of the lining there is a special diagram showing the terminals of the block.
- Using a piece of wire, cable or paper clip, you need to make a jumper that is mounted between the pins numbered TE1 and E1.
- The key is inserted into the lock and the ignition is activated. When conducting diagnostics, the heating and air conditioning systems must be turned off.
- During the test, you need to look at the Check Engine LED indicators (for diagnosing the power unit) and at O/D (for the gearbox). The user must record the number of blinks of the light bulb, as well as the intervals.
Pin designation on the DLC diagnostic block
You can determine the absence of malfunctions in the operation of the internal combustion engine (ICE) and gearbox by two symptoms:
- LED lights blinked evenly at the same interval and duration 11 times;
- The Check indicator blinks continuously and evenly at intervals of 4.5 seconds.
If there is no contact diagram on the cover or it has been erased, you can determine the required pins as follows:
- The car's ignition system turns on.
- One of the contact elements of the light indicator is connected to any standard engine ground bolt.
- The second output of the light bulb is connected in turn to each contact of the diagnostic block.
- At the moment when the Check indicator lights up on the dashboard, we can conclude that the required pin has been found.
To read the code you need to count the LED blinks:
- when a combination appears, the LED blinks quickly, lights up for a few tenths of one second;
- the time interval between decimal and unit readings will be no more than 1.5 s;
- the pause between each subsequent code will be 2.5 seconds;
- series of codes for various problems are separated by a pause of 4.5 s.
Video: Toyota car self-diagnosis
The JDM27 channel in its video showed the process of diagnosing the engine and automatic transmission of a Toyota car.
How to carry out self-diagnosis of a car?
Toyota cars usually have 3 blocks of dynamic connectors: DLC 1, DLC 2 and DLC 3. These blocks can be either under the hood or inside the cabin. It all depends on the year of manufacture of the car. Without a special scanner, you can carry out self-diagnosis of the car. This will require wire. It should be bent like the letter P.
To carry out diagnostics, first of all, you need to turn off the ignition in the car. Next you need to do the following:
Next you need to start the car and check the CHECK indicator. Based on this, the error number can be determined.
It is not difficult to determine the error code. You need to count how many times the indicator flashes at intervals of half a second or less. If the light stops blinking for about 1.5-2.5 seconds, then the next blinking will indicate the second digit. For example, the indicator may blink 2 times with an interval of half a second, then pause for 1.5-2.5 seconds and blink 3 times again. This means error code 23.
There may be a situation when several problems are detected at once. Then there will be more than one code. A pause between flashes of 2.5-4.5 seconds means a transition to the next code.
If the indicator blinks more than 11 times without pauses, then there are no problems with the transmission or engine.
It will be easier for the driver to determine the essence of the problem if there is a special auto scanner for diagnostics. It can be used to configure and diagnose the on-board computer. Without a scanner, you need to decipher error codes yourself using a table.
There are errors mainly related to malfunctions:
On Toyota Rav 4, the error code usually consists of five characters, but there are also two-digit ones.
How to reset the error?
To clear a fault code, perform the following steps:
- The car's ignition system turns on.
- On the diagnostic block, to reset the memory of the control unit, contacts TC and E1 are closed.
- Over the next three seconds, the user must press the brake pedal at least 8 times.
- Then you need to make sure that the LED indicator blinks with a pause of 0.5 seconds.
- The ignition is turned off and the jumper is disconnected from the pins. If the error codes are successfully cleared, the anti-lock brake indicator will not illuminate on the instrument panel.
You can use a computer to remove combinations of faults. If the diagnostics were performed using a laptop, software is used to reset the memory.
More category errors
B1907/74B1908/74B1920/77B1921/77B1922/77B1923/77B1925/78B1926/78B1927/78B1928/78B2796/99B2797/99B2798/99C0226C0236C0246C0256 C0273C0274C0278C0279C0371C1201C1203C1210C1225C1232C1241C1243C1245C1271C1272C1279C1300C1336C1361C1381C1401C1402C1403C1404C1405 C1406C1407C1408C1413C1414C1415C1416C1417C1425C1427C1428C1432C1433C1434C1436C1437C1439C1440C1442C1443C1445C1511C1512C1513C1514 C1515C1516C1517C1524C1531C1532C1533C1534C1535C1551C1552C1553C1554C1555C1581C1582C1611C1612C1613C1621C1622C1625C1626C1627C1628 C1645C164AC164EC1657C1658C1659C1662C168BSee all errors →
The cost of diagnosing errors for Ford at service stations in Moscow and St. Petersburg
Approximate prices for computer diagnostics of faults:
| City | Company name | Address | Phone number | Price |
| Moscow | North Motors | St. Dubninskaya, 83 | +7 | 2500 rub. |
| Silver elephant | St. Pyalovskaya, 7 | +7 | 3500 rub. | |
| Saint Petersburg | Automagic | St. Uchitelskaya, 23 | +7 | 2000 rub. |
| ClinliCar | Bolshoy Sampsonievsky Ave., 61k2 | +7 | 3000 rub. |